Figure 2.
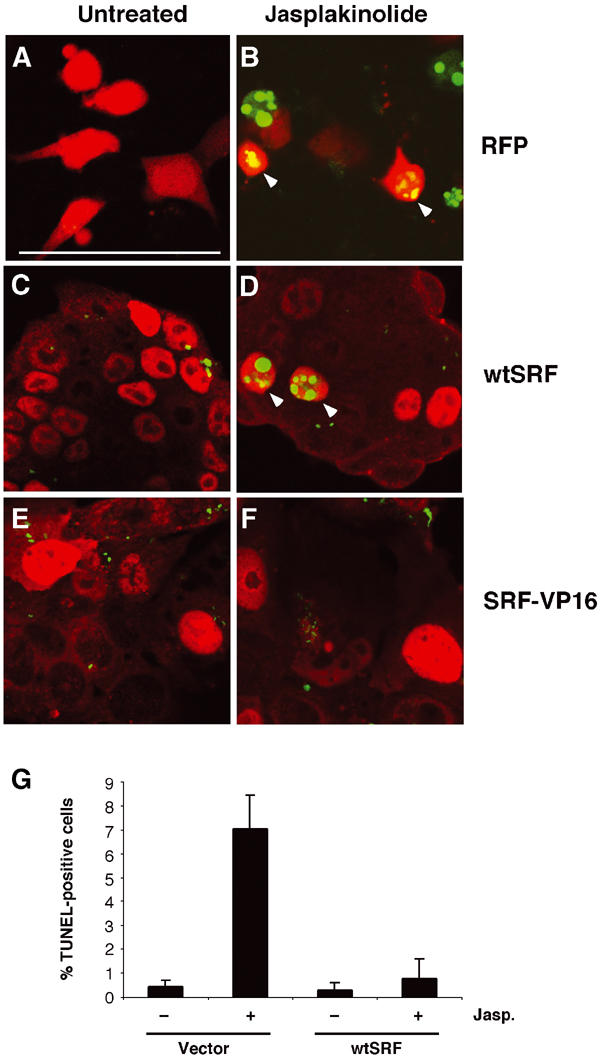
Activated SRF is sufficient to rescue survival of ES cells after jasplakinolide treatment. 100 Srf(−/−) ES cells were transiently transfected with expression vectors encoding red fluorescent protein (RFP; A, B), wt SRF (wtSRF; C, D), or constitutively active SRF-VP16 (E, F). At 48 h after transfection, cells were treated for 24 h either with solvent control (A, C, E; untreated) or with 10 nM jasplakinolide (B, D, F). Transfected cells were identified by their red fluorescence. RFP was detected directly (A, B) and SRF- and SRF-VP16-expressing cells were identified by immunofluorescent staining (red) using antibodies against SRF (C, D) or VP16 (E, F), respectively. Apoptotic cells were visualized by TUNEL staining (green). Note the presence of double positive cells in (B) and, at very low frequency, in (D) (arrowheads), as well as the absence of such cells in (F). Bar=50 μm. (G) Apoptotic Srf(−/−) ES cells were quantified by FACS of untreated or jasplakinolide-treated cultures transfected with either empty vector or wtSRF. Values represent the mean of two independent experiments ±s.d.
