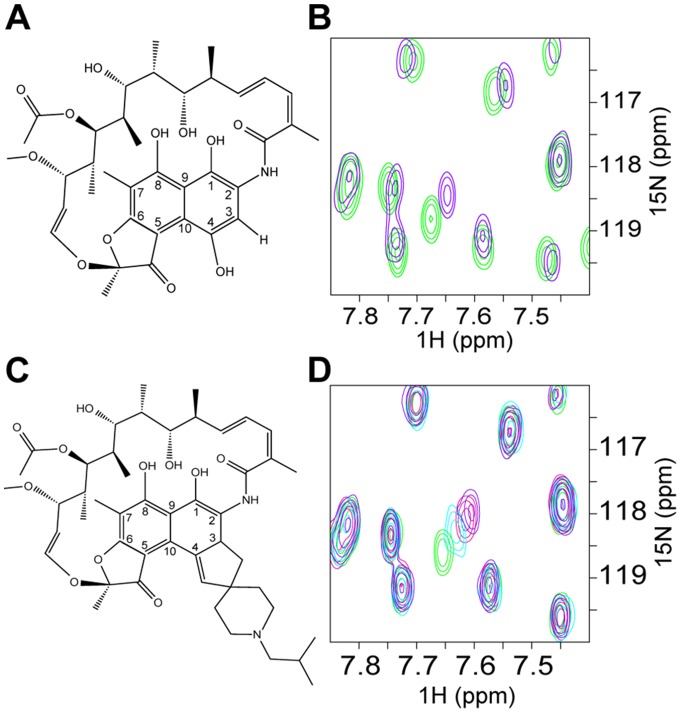
Figure 2. Rifamycin SV and its derivative, rifabutin, bind directly to the BCL6-POZ domain.
Schematic diagram to compare the structures of (A) rifamycin SV and (C) rifabutin. These two compounds differ with respect to the side chains on C-3 and C-4. (B) and (D) TROSY 1H,15N HSQC spectra of 280 μM BCL6-POZ domain. (B) Chemical shift changes due to rifamycin SV. An overlay of the spectra of BCL6-POZ domain alone (green) and in the presence of a 16∶1 molar ratio of rifamycin (purple). (D) Chemical shift changes due to rifabutin with an overlay of the spectra of BCL6-POZ domain alone (green) and in the presence of 4∶1 (light blue), 8∶1 (red) and 16∶1 (purple) molar ratios of rifabutin.