Figure 5.
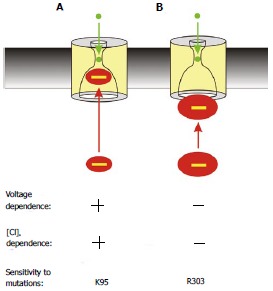
Two distinct proposed mechanisms of block by cytoplasmic anions. A: The effects of most blockers are voltage- and Cl- dependent (as described in Figure 2) and are sensitive to mutations that remove the positive charge at K95; B: The large multivalent anion suramin blocks the channel in a voltage- and Cl- independent fashion, and its effects are dependent on a positive charge at R303 but independent of K95. This is interpreted as the large suramin molecule blocking the cytoplasmic entrance to the pore; at a site that does not involve entering significantly into the transmembrane electric field or approaching close enough to Cl- ions inside the pore to experience repulsive electrostatic interactions.
