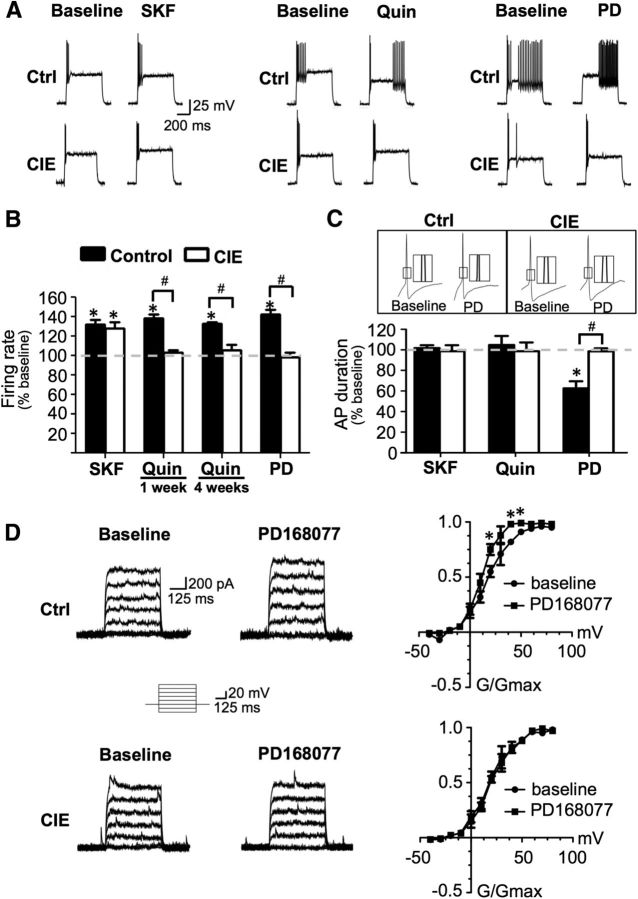
Figure 6.
D2/D4 receptor modulation of evoked firing in FS interneurons was attenuated in CIE-exposed rats. A, B, Bath application of a D1 receptor agonist increased evoked firing in both controls and CIE rats. In contrast, bath application of either a D2 or D4 agonist increased firing in control animals, but this effect was absent in slices from CIE animals at 1 and 4 weeks of withdrawal from CIE exposure. C, The increased firing rate observed following D1 and D2 receptor stimulation in controls did not occur via changes in spike duration and this was not affected by CIE. However, the increase in firing observed with D4 receptor stimulation occurred at least in part due to a reduction in action potential duration and this effect was absent in CIE rats. *p < 0.05 versus baseline, paired t test, n = 4–7 cells from 4 to 6 rats. D, Kv3.1/3.2 currents were enhanced by bath application of a D4 receptor agonist in control slices (top) but were not affected by D4 receptor stimulation in CIE slices (bottom). *p < 0.05 versus baseline, paired t test, n = 4–5 cells from four rats. Quin, quinpirole, PD, PD168077; SKF, SKF38393.