Figure 1.
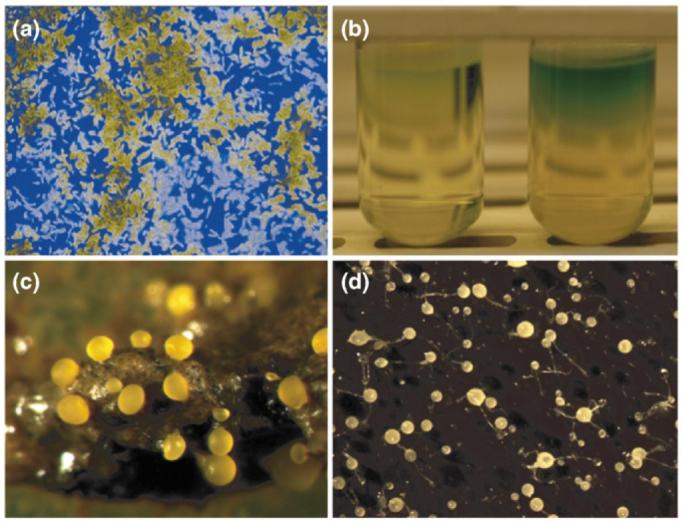
Microbial social behaviors. (a) Early-stage Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm containing two strains, one labeled with cyan fluorescent protein and the other with yellow fluorescent protein. Biofilms contain numerous shared group products, including the extracellular polymeric substances that produce a matrix surrounding the cells. (b) Two strains of P. aeruginosa in LB medium, showing the pigments of siderophores, which are extracellular molecules released by the bacteria to scavenge iron. (c) Fruiting bodies of the social bacterium Myxococcus xanthus. (d) Fruiting bodies of the social ameba (i.e. slime mold) Dictyostelium discoideum. Photo in part c kindly provided by Michiel Vos.
