Figure 2. The Cas protein families required for crRNA biogenesis and targeting in the three CRISPR-Cas types.
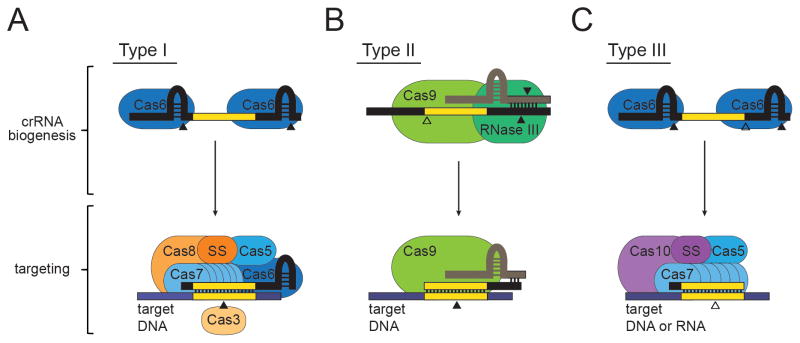
(A) In Type I CRISPR-Cas systems, a Cas6 endoribonuclease cleaves within repeat sequences (colored black) to generate mature crRNAs. CrRNAs then assemble with a targeting complex that includes Cas6, the Type I signature subunit Cas8, and members from the Cas5 and Cas7 families. An independent small subunit (SS) may be present in some subtypes, or found fused to Cas8. The DNA target (colored blue) is cleaved by Cas3, a protein that is not associated with the complex. (B) In Type II CRISPR-Cas systems, a trans-encoded CRISPR-RNA (tracrRNA, colored beige) binds crRNA repeats through base-pair complementarity, and facilitates RNase III-mediated cleavage of both RNAs. CrRNA biogenesis requires additional cleavage by an unknown nuclease to generate mature crRNAs. A single large multi-domain protein, Cas9, is required for both crRNA biogenesis and DNA target cleavage. (C) In Type III CRISPR-Cas systems, crRNA biogenesis is accomplished by Cas6-mediated cleavage within repeats and additional trimming by an unknown nuclease. The Type III targeting complex contains Cas10, the large signature subunit, Cas5, and distinct members of the Cas7 family. An additional subtype-specific small subunit (SS) is also a present in Type III complexes. Targeting against DNA and RNA in Type III systems is catalyzed by an unknown nuclease. Solid arrows represent nucleolytic cleavage events carried out by the protein on top of which they appear, and open arrows indicate cleavage events carried out by unknown nucleases.
