Abstract
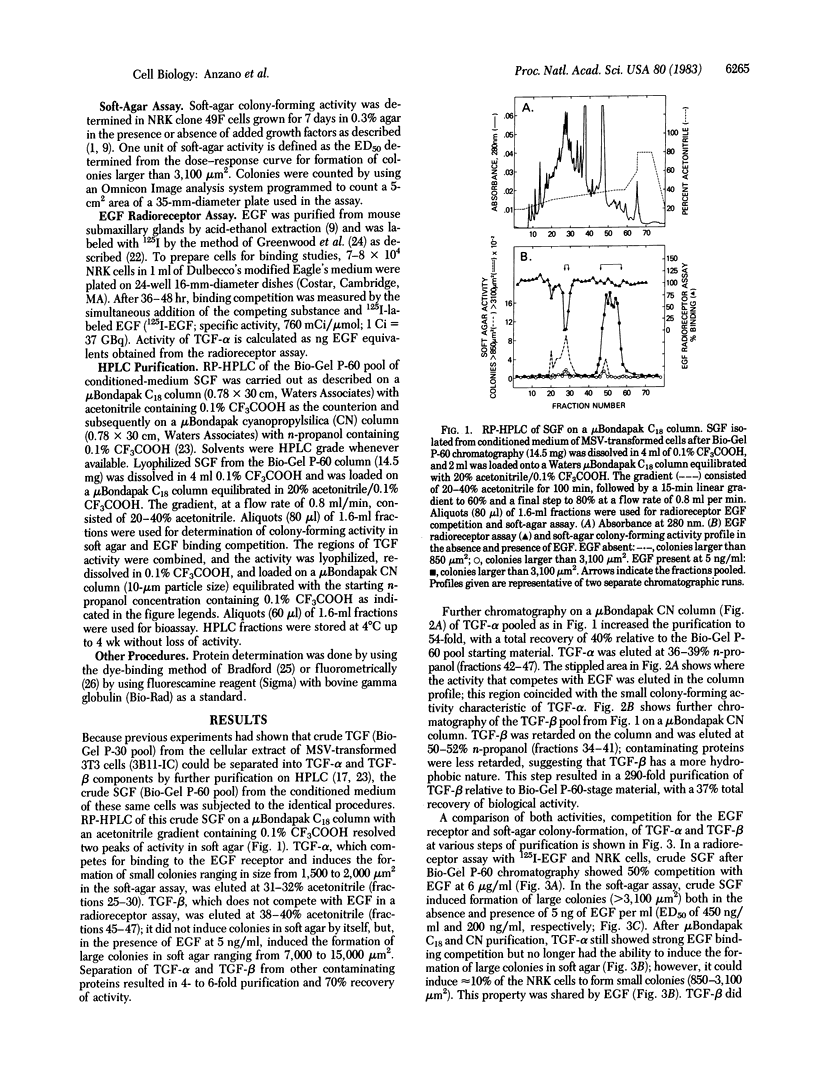
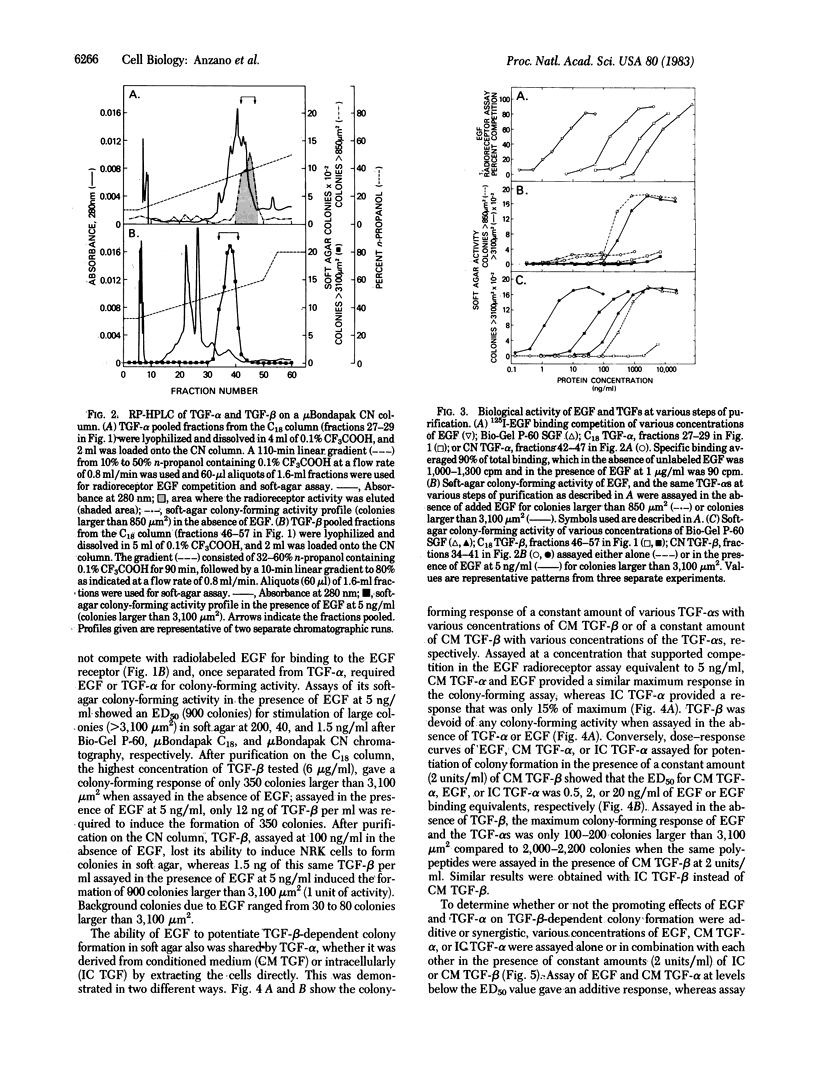
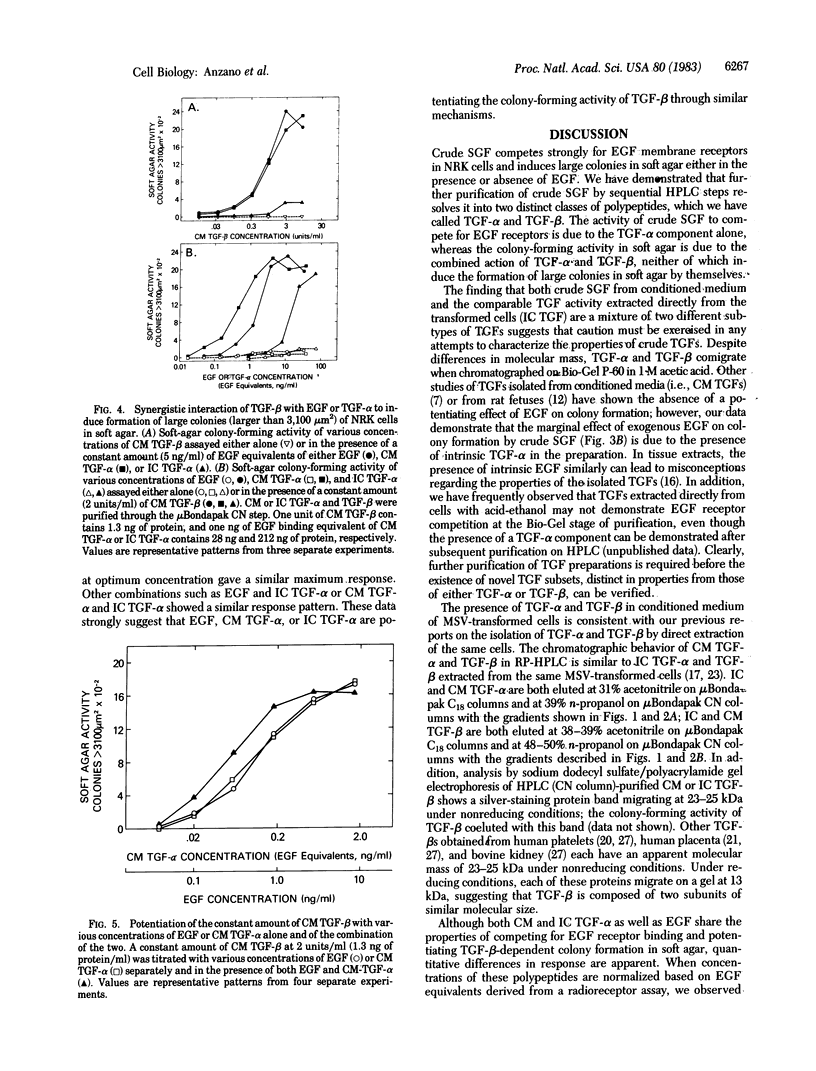
Sarcoma growth factor (SGF) derived from conditioned medium of Moloney sarcoma virus-transformed cells and partially purified by gel filtration (crude SGF) has been characterized by its ability both to compete with epidermal growth factor (EGF) for binding to membrane receptors and to induce anchorage-independent growth of untransformed cells. We now show that further purification of crude SGF by reverse-phase HPLC on muBondapak C18 and CN columns at pH 2 resolves it into two distinctly different polypeptides, which we call types alpha and beta transforming growth factors (TGFs). Type alpha TGF (TGF-alpha), but not type beta TGF (TGF-beta), competes for binding to the EGF receptor and induces the formation of small colonies (1,000-2,000 micron2) of normal rat kidney cells in soft agar. Both TGF-beta and EGF or TGF-alpha must be present in order to induce the formation of large colonies (7,000-15,000 micron2). Based on EGF competing equivalents as determined from a radioreceptor assay with 125I-labeled EGF in normal rat kidney cells, the relative ability of EGF and TGF-alpha to potentiate TGF-beta-dependent colony formation is in the order conditioned-medium TGF-alpha greater than EGF greater than intracellular TGF-alpha. Suboptimal concentrations of the same polypeptides give additive potentiation of the TGF-beta-dependent colony-forming response; saturating levels potentiate a similar maximum response whether used alone or in various combinations. The data indicate that the EGF-competing activity of crude SGF is due to its TGF-alpha component alone, whereas the soft-agar colony-forming activity is due to the combined action of two distinct polypeptides, TGF-alpha and TGF-beta.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anzano M. A., Roberts A. B., Meyers C. A., Komoriya A., Lamb L. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B. Synergistic interaction of two classes of transforming growth factors from murine sarcoma cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Nov;42(11):4776–4778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzano M. A., Roberts A. B., Smith J. M., Lamb L. C., Sporn M. B. Purification by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of an epidermal growth factor-dependent transforming growth factor. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;125(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Komoriya A., Meyers C. A., Miller D. M., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta in human platelets. Identification of a major storage site, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7155–7160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Stoscheck C. M., Preston Y. A., DeLarco J. E. Antibodies to the epidermal growth factor receptor block the biological activities of sarcoma growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5627–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs C. B., Proper J. A., Tucker R. F., Moses H. L. Serum contains a platelet-derived transforming growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5312–5316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Larco J. E., Preston Y. A., Todaro G. J. Properties of a sarcoma-growth-factor-like peptide from cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive sarcoma virus. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Oct;109(1):143–152. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Sarcoma growth factor (SGF): specific binding to epidermal growth factor (EGF) membrane receptors. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Feb;102(2):267–277. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041020218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolik C. A., Dart L. L., Meyers C. A., Smith D. M., Sporn M. B. Purification and initial characterization of a type beta transforming growth factor from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3676–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krycève-Martinerie C., Lawrence D. A., Crochet J., Jullien P., Vigier P. Cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus release transforming growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Dec;113(3):365–372. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J. Human transforming growth factor. Production by a melanoma cell line, purification, and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5220–5225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Czech M. P., Iwata K., DeLarco J. E., Todaro G. J. Affinity labeling of a transforming growth factor receptor that does not interact with epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6822–6826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Pathak M., Magun B. E. Identification of an epidermal growth factor-related transforming growth factor from rat fetuses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):761–769. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Branum E. L., Proper J. A., Robinson R. A. Transforming growth factor production by chemically transformed cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Jul;41(7):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Fulton R. J., Kaplan P. L. Kirsten murine sarcoma virus transformed cell lines and a spontaneously transformed rat cell-line produce transforming factors. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Oct;105(1):163–180. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proper J. A., Bjornson C. L., Moses H. L. Mouse embryos contain polypeptide growth factor(s) capable of inducing a reversible neoplastic phenotype in nontransformed cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Feb;110(2):169–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Lamb L. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B. New class of transforming growth factors potentiated by epidermal growth factor: isolation from non-neoplastic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5339–5343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Frolik C. A., Anzano M. A., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factors from neoplastic and nonneoplastic tissues. Fed Proc. 1983 Jun;42(9):2621–2626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Lamb L. C., Newton D. L., Sporn M. B., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors: isolation of polypeptides from virally and chemically transformed cells by acid/ethanol extraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3494–3498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Moschera J. High-performance liquid chromatography and picomole-level detection of peptides and proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):7–16. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E. Growth factors produced by sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4147–4154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Fryling C., De Larco J. E. Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Ranchalis J. E., Todaro G. J. Mouse embryonic transforming growth factors related to those isolated from tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Feb;42(2):590–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Sherwin S. A., Ranchalis J., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors in the urine of normal, pregnant, and tumor-bearing humans. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Oct;69(4):793–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twardzik D. R., Todaro G. J., Marquardt H., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Transformation induced by Abelson murine leukemia virus involves production of a polypeptide growth factor. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):894–897. doi: 10.1126/science.6177040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwiebel J. A., Davis M. R., Kohn E., Salomon D. S., Kidwell W. R. Anchorage-independent growth-conferring factor production by rat mammary tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):5117–5125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Growth factors from murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4001–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


