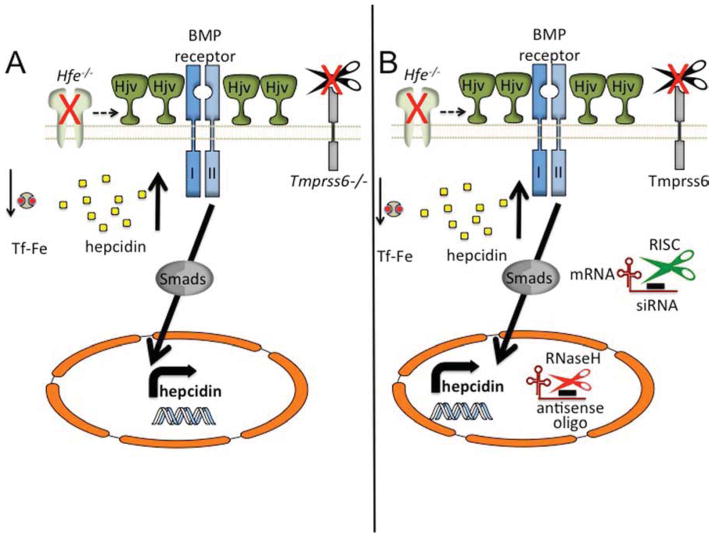
Figure 4. Modulation of hepcidin expression through genetic or pharmacological targeting of Tmprss6.
Loss of all endogenous Tmprss6 protein (A) leads to elevated levels of Hjv, the Bmp co-receptor, on the cell membrane. Significant hepcidin expression causes suppressed iron levels and a hypochromic, microcytic anemia, even in a mouse lacking Hfe. (B) Targeting of Tmprss6 thorough pharmacological means. Targeting of Tmprss6 siRNA to the liver in lipid nanoparticle (LNP)–formulated siRNAs, or by antisense oligonucleotide technology, leads to diminished Tmprss6 mRNA expression through classic RISC-mediated (cytoplasmic) or RnaseH-mediated (nucleus) suppression, respectively. Suppression of Tmprss6 causes elevated levels of Hjv to remain on the cell membrane, triggering heightened hepcidin expression and ameliorating the Hfe−/− phenotype.