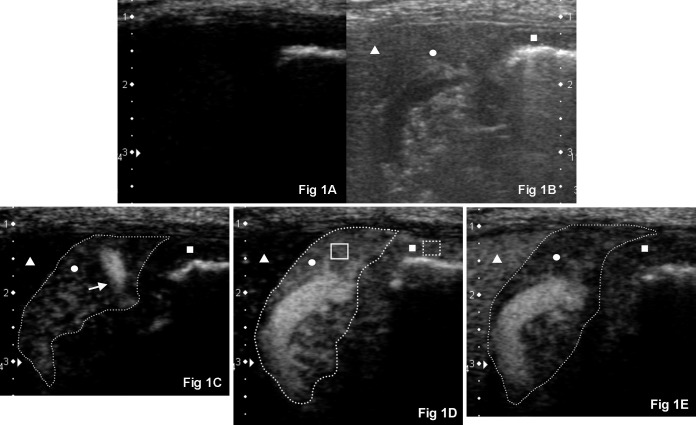
Fig. 1.
CEUS images before and after bolus injection. Right intercostal approach imaging the transverse view of the normal right pancreatic limb (circle, outlined by a dashed line) and proximal descending duodenal mucosa (square) in a representative adult dog (dorsal is to the left, ventral is to the right and medial is to the bottom). (A) CEUS at 0 sec. Baseline tissue echo components of the pancreatic parenchyma and duodenal mucosa were minimal in the CEUS mode. (B) Corresponding twin view B-mode image of (A). (C) CrPDA (white arrow) was more enhanced compared to the pancreatic parenchyma at 8 sec after bolus injection of contrast agent. Duodenal mucosa was still unenhanced. (D) Both the pancreatic parenchyma and duodenum reached its PI (shown here 12 sec after bolus injection of contrast agent). The pancreas is well delineated from the unenhanced neighboring liver (triangle). Region of interests (ROIs) are manually placed in the pancreatic parenchyma (solid box) and duodenal mucosa (dashed box) to measure the tissue intensity. (E) Contrast washing out of the pancreatic parenchyma and duodenal mucosa at 20 sec.