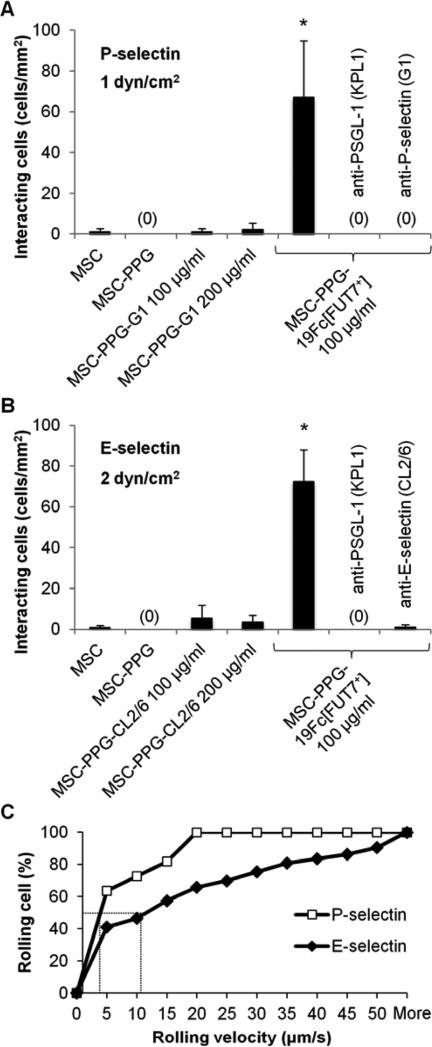
Fig. 5. MSC-PPG-19Fc[FUT7+] binding to P- and E-selectin in microfluidic flow chamber.
A-B. 2-5×106 MSCs/mL immobilized with either 100 μg/mL 19Fc[FUT7+], 100-200 μg/mL anti-P-selectin mAb G1 or 100-200 μg/mL anti-E-selectin mAb CL2/6 were perfused over either P-selectin bearing CHO-P cells at a wall shear stress of 1 dyn/cm2 (panel A) or E-selectin bearing stimulated HUVECs at 2 dyn/cm2 (panel B). Only the MSC-PPG-19Fc[FUT7+] cells bound the selectin bearing substrate. Cell interaction was specifically blocked using anti-PSGL-1 mAb KPL1, anti-P-selectin mAb G1 or anti-E-selectin mAb CL2/6 as indicated. Data are mean ± SD for 3-4 independent experiments. * indicates P < 0.001 with respect to all other conditions. C. Cumulative rolling velocity plot showing median rolling velocity of 3 μm/s when MSC-PPG-19Fc[FUT7+] roll on P-selectin/CHO-P cells at 1 dyn/cm2 and 11.5 μm/s for rolling on E-selectin/ HUVECs at 2 dyn/cm2. The rolling characteristics of 190 cells were analyzed and binned from three independent runs.