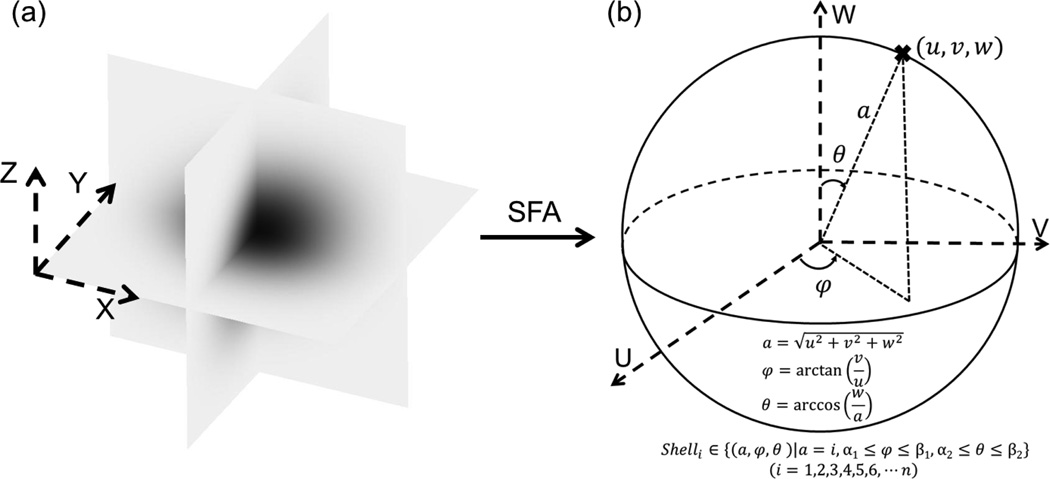
Figure 1.
An illustration of the SFA and averaging the diffusivity in the frequency domain over a shell. In the SFA, the solute concentration distribution is transformed from the spatial domain (a) to the frequency domain (b) by using the Fourier transform. In the frequency domain, the diffusivity D(u,v,w) is averaged over a shell of a spherical surface to obtain all components of the 3D diffusion tensor. The level of shell is defined by the radius a (i.e., commonly positive integers) and the range of shell is determined by azimuthal angle φ and polar angle θ.