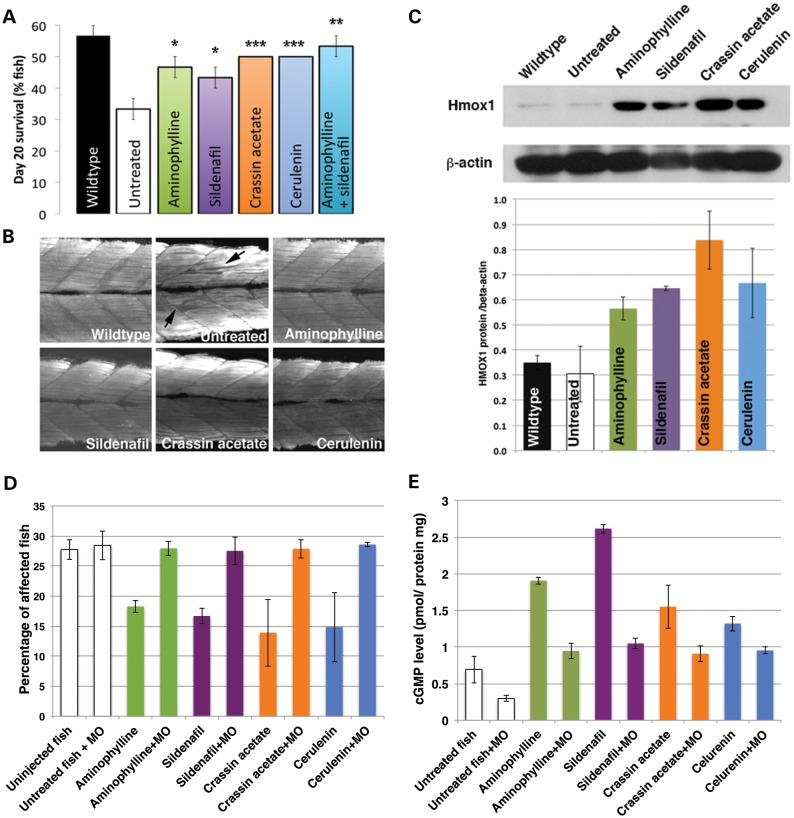
Figure 2.
Dystrophic muscle restoration via increased heme oxygenase signaling. (A) Treatment with multiple components of the Hmox1 signaling pathway results in increased survival of dystrophin-null fish, sapje fish (P = 1.16e-05, repeated-measures ANOVA. *For aminophylline, sildenafil: P ≤ 0.05, **for aminophylline + sildenafil: P ≤ 0.01, ***for cerulenin, crassin acetate: P ≤ 0.005, n = 10 in triplicate). (B) Normal skeletal muscle structure in treated dystrophin-null fish, sapje fish (20 dpf). Skeletal muscle in treated dystrophin-null fish was immunostained with anti-myosin heavy chain. Arrows point to common breaks in untreated dystrophic muscle. (C) Upregulation of Hmox1 expression in surviving chemically treated dystrophin-null fish. Hmox1 expression in surviving chemically treated dystrophin-null fish was analyzed with immunoblot (n = 3). Treatment with each candidate drug (aminophylline: P = 0.038, sildenafil: P = 0.012, crassin: P = 0.0095 and cerulenin: P = 0.045, compared with those of untreated dystrophin-null fish, t-test, n = 3) upregulated Hmox1 expression. (D) Birefringence phenotype rate in sapje-like fish and an anti-sense morpholino oligonucleotides-injected sapje-like fish after treatment with candidate drugs. Treatment with candidate drugs (aminophylline, sildenafil, cerulenin and crassin acetate) has significant effects on the improvement of reduced birefringence phenotypes in dystrophin-deficient skeletal muscle (40 fish in triplicate). After injection of an anti-sense morpholino oligonucleotides (MO) against the expression of zebrafish Hmox1 to inhibit zebrafish Hmox1 expression, the treatment with candidate drugs does not have significant effects on the improvement of reduced birefringence in skeletal muscle. (Uninjected fish versus Hmox1-MO-injected fish; aminophylline: P = 0.00079, sildenafil: P = 0.0043, crassin acetate: P = 0.027 and cerulenin: P = 0.028, t-test, n = 3). (E) Measurement of cGMP levels in sapje-like fish and Hmox1 MO-injected sapje-like fish after treatment with candidate drugs. Treatment with candidate drugs (aminophylline, sildenafil, crassin acetate and cerulenin) significantly has effects in increasing cGMP level (40 fish in triplicate). After injection of an MO against the expression of zebrafish Hmox1, the treatment with candidate drugs still shows strong effects in increasing cGMP levels to almost normalized levels of the uninjected fish. (Uninjected fish versus Hmox1-MO-injected fish; untreated fish: P = 0.040, aminophylline: P = 0.00028, sildenafil: P = 0.000018, crassin acetate: P = 0.044 and cerulenin: P = 0.010, t-test, n = 3).