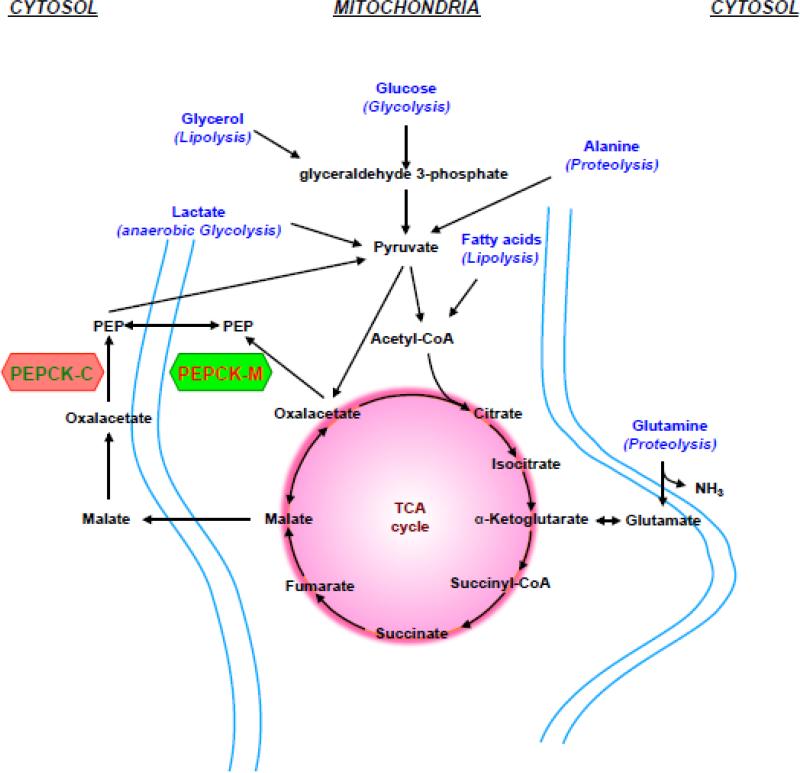
Figure 3. Gluconeogenic substrates entering the gluconeogenic pathway.
Graph shows entry point of gluconeogenic substrates, such as lactate, glycerol or amino acids. Both PEPCKs synthesize PEP from OAA that can feed the TCA cycle (anaplerosis) or serve for various biosynthetic processes (cataplerosis), such as gluconoegenesis. Alanine and glutamine are the main amino acids in the blood and arise during starvation from muscular protein breakdown (proteolysis). Likewise, fatty acids and glycerol are released from triglyceride breakdown (lipolysis) during fasting. Unlike glycerol, acetyl-CoA (fatty acid breakdown) does not contribute to cataplerotic OAA or PEP production or other gluconeogenic intermediates. Glycerol and glucose enter via glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Lactate forms in the muscle during anaerobic glycolysis and enters the gluconeogenic pathway via pyruvate and is the main gluconeogenic precursor in the kidney and liver.