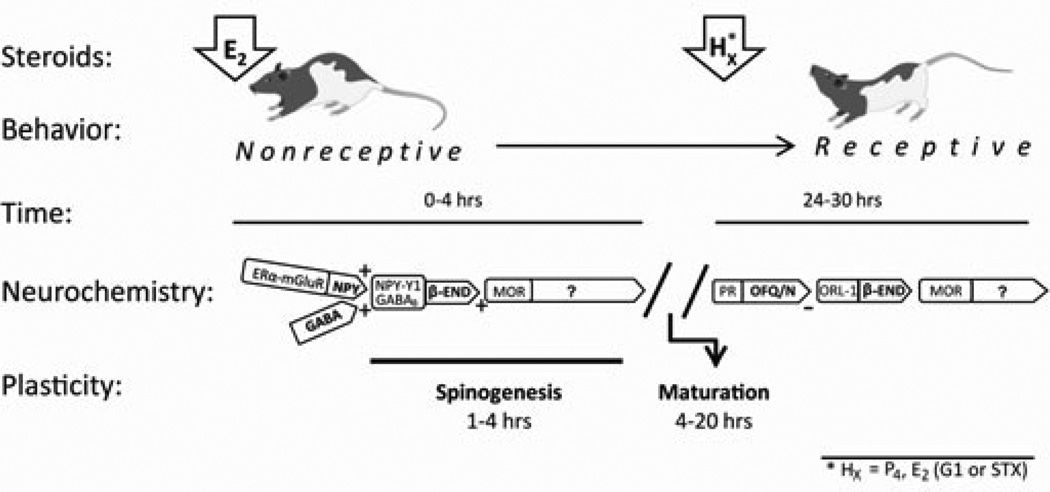
Figure 1.
A schematic of the timecourse of events initiated by estradiol (E2) and progesterone (P4) leading to sexual receptivity in the rat. This timeline begins with an ovariectomized rat treated with E2 to activate β-endorphin (β-END) neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARH). In the ARH, estrogen receptor-α (ERα), trafficked to the cell membrane by E2, transactivates type 1a metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1a) stimulating the release of NPY and GABA onto β-END neurons (activating NPY-Y1 and GABAB receptors, respectively). The relatively rapid, and membrane ERα-dependent, action leads to the release of β-END onto medial preoptic nucleus (MPN) neurons expressing μ-opioid receptors (MORs) – inhibiting lordosis behavior for approximately 20–24 hrs. Simultaneously acting through membrane ERα complexed with mGluR1a (mERα-mGluR1a), E2 induces the formation of dendritic spines in the ARH. While these spines are immature and probably not functional, without this spinogenesis lordosis behavior is not induced by E2. In addition to the activation of MOR and spinogenesis, during this initial phase after E2, the appropriate proteins, neuropeptides and receptors are transcribed. The initial “priming” phase is dependent on E2, but the behavioral “triggering” phase (24–30 post E2) that follows is dependent on either E2 or progesterone (P4). This activation requires GABA and GABAB receptors. For behavior to ensue, P4 (or E2) must relieve the MOR inhibition and induce functional spines. In the ARH, acting through it cognate receptor ORL-1, orphanin FQ/nociception (OFQ/N) inhibits β-END release relieving the MOR blockade of the ventromedial hypothalamus As with the initial action of E2, GABAB receptor activation is critical. While P4 is the signal for triggering lordosis behavior in the intact rat, experimentally, E2 acting through GPR30 can substitute for P4 and trigger lordosis.