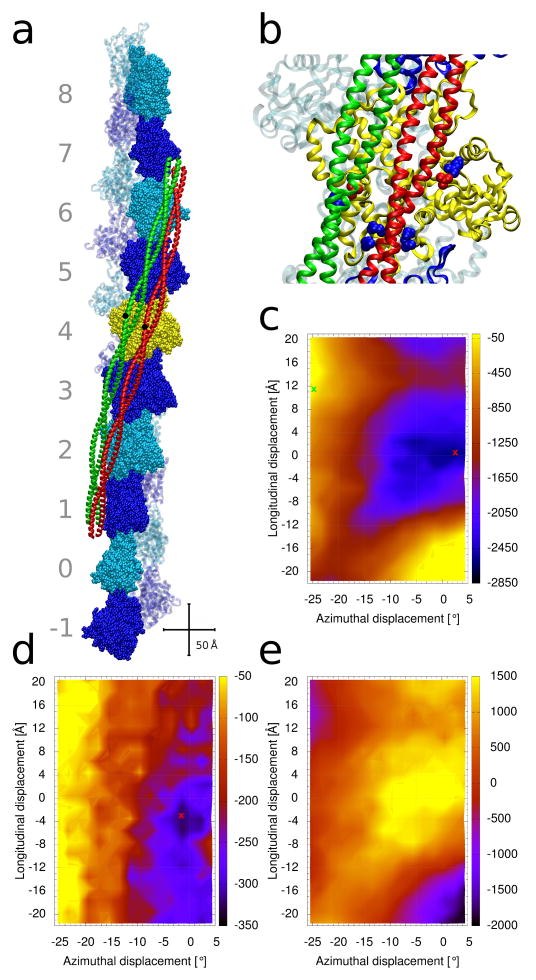
Figure 1.
Tropomyosin positions on the surface of F-actin. (a) Structure of F-actin complexed with tropomyosin in either the troponin and myosin-free A-position (colored red) [6], or in the S1-decorated M-position (green) [12]. Ten actin-pairs (each pair shown in space-filling and ribbon representations) are colored alternatively in dark-blue and cyan. The pairs are numbered from −1 to 8. The actin filament is oriented with its pointed end facing up; hence, the N-terminus of tropomyosin also faces up. Centrally located tropomyosin residue 125 is highlighted in black as a reference point to indicate the relative sliding of tropomyosin between positions. Crisscrossing scale bars – 50 Å. (b) Enlarged view of the central yellow actin subunit in (a), showing some of the acidic and basic actin residues of actin which form attractive interactions with tropomyosin when it is in the myosin-free A-position (red and blue spheres, respectively, which highlight residues D25 and R28 (top right pair), K147, K326, K328 (bottom cluster)). D311 and K315 (left) interact with tropomyosin in the M-position (green) [7,12]. (c–e) Energy landscapes, with the energy levels (in kcal/mol) shown by the color scales on their right. At each point of the landscape, tropomyosin was repositioned longitudinally and azimuthally (see Methods) and the energy of the complex was optimized. The [0, 0] position corresponds to the tropomyosin position described by the Li et al. [6] (red ribbon location in panel (a)). (c) Contributions from the Coulombic interaction energy. The energy minimum is indicated by a red cross. The open M-state position of tropomyosin [12] is indicated by a green cross. (d) Corresponding total potential energy and (e) the contribution from the solvation energy (see Methods).