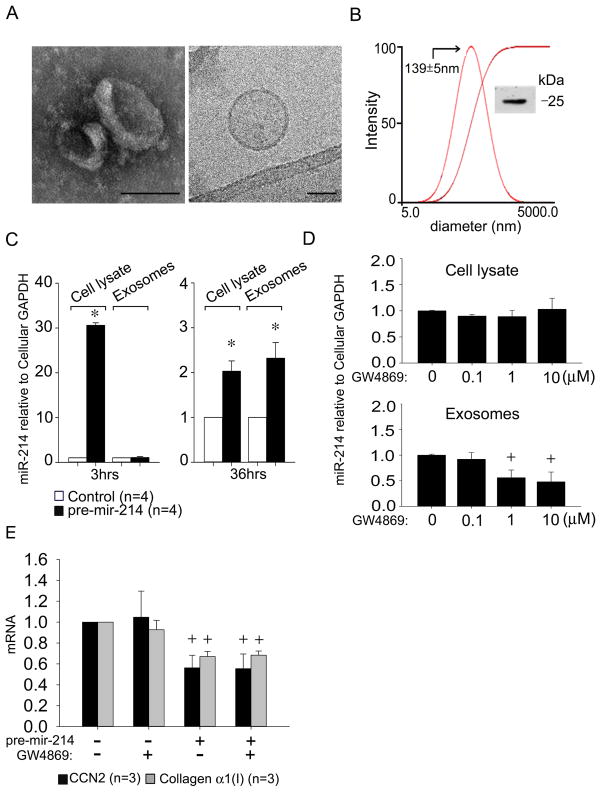
Fig. 4. Identification and characterization of mouse HSC-derived exosomes.
Exosomes were isolated by sequential centrifugation of conditioned medium from P6 mouse HSC. (A) TEM (left) and cryogenic TEM (right). Scale bar: 100nm (left), 50nm (right). (B) Dynamic light scattering and zeta potential analysis, showing the presence of ~140nm particles (−26mV). Inset: CD9 Western blot. (C) RT-PCR of cellular or exosomal microRNA isolated from control or pre-mir-214-transfected cells after 3hrs or 36hrs, normalized to cellular GAPDH. (n=4 independent experiments performed in triplicate, *P <0.001 vs. control group). Ct value = 38 for endogenous exosomal miR-214 in control cells at 3hrs. (D) Cellular or exosomal miR-214 levels assessed by RT-PCR in pre-mir-214-transfected HSC after 24 hrs treatment with GW4869, with data normalized to cellular GAPDH. (n=4 independent experiments performed in triplicate, +P <0.05 vs. Control group). (E) CCN2 or collagen α1(I) expression in control or pre-mir-214-transfected HSC in the presence or absence of 10 μM GW4869.