Figure 6.
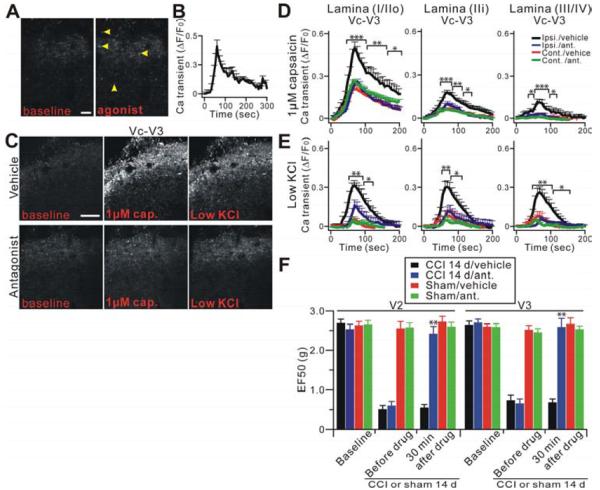
Functional 5-HT3 receptors are present on central terminals of primary sensory neurons and mediate the sensitization of central terminals. (A) Representative Pirt-GCaMP3 imaging of Vc slices treated with 5-HT3AR agonist by bath application. Many central terminals in Vc after nerve injury were activated by the agonist (yellow arrowheads; n=9). Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) Time course of the amplitude of the Ca2+ transient that was evoked by 5-HT3AR agonist from (A). (C) Central terminals in V3 of ipsilateral Vc slices after nerve injury were bath pretreated with either the 5-HT3AR antagonist (lower panels) or vehicle (upper panels) for 30 min and then were activated by capsaicin (1 μM) or low KCl. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D and E) Strong hypersensitivity of central nerve fibers and terminals in Vc after nerve injury is significantly blocked by the antagonist. Time course of the amplitude of the Ca2+ transient that was evoked by capsaicin (1 μM) or low KCl application at V3 in Vc. Ipsi., ipsilateral (n=15); cont., contralateral (n=14); ipsi./ant., ipsilateral antagonist (n=12); cont./ant., contralateral antagonist (n=8). (F) Mechanical hyperalgesia was tested in V2 (injured) or V3 (uninjured) region at 14 days before and 30 min after intra-Vc 5-HT3AR antagonist (n=8) or vehicle (n=6) injection in nerve injury or sham mice (n=8, n=6 for antagonist or vehicle, respectively). *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.