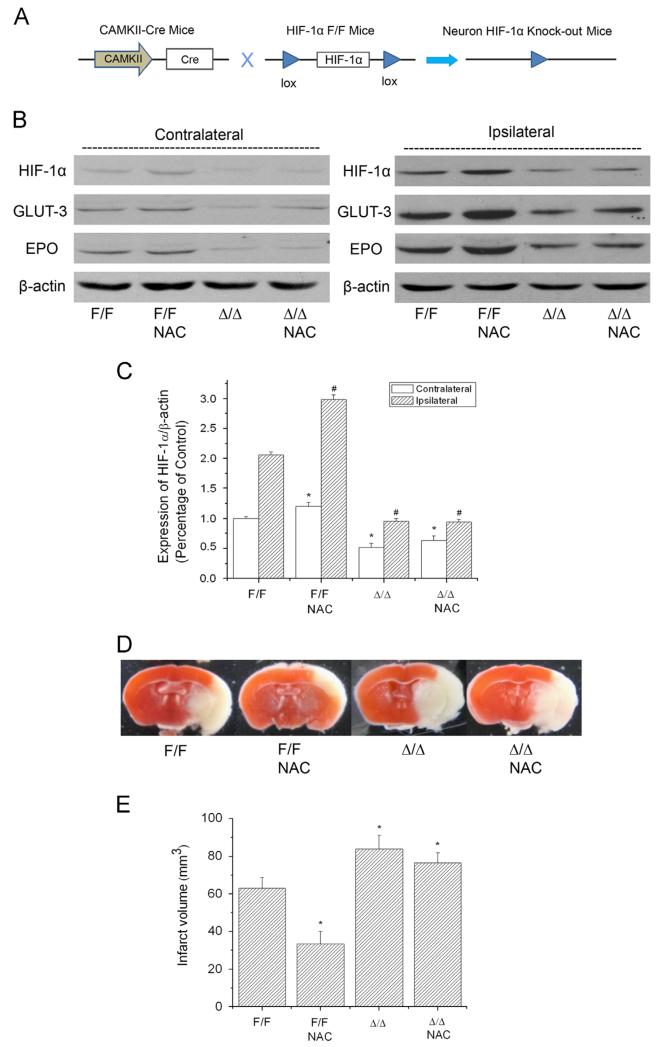
Fig. 5.
Effect of NAC on HIF-1 expression and ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain infarction in wild-type (HIF-1αF/F) and neuronal HIF-1α-deficient (HIF-1αΔ/Δ) mice. The protein levels of HIF-1α, GLUT-3, and EPO were analyzed by Western blotting in the brains of mice subjected to 90 min ischemia and 24 h reperfusion. Mice received NAC (240 mg/kg, ip) at 30 min before the onset of ischemia. (A) Schematic of the neuron-specific HIF-1α-knockout mouse model. (B) Representative Western blots of HIF-1α and its downstream proteins GLUT-3 and EPO. (C) Quantification of the HIF-1α protein level in contralateral and ipsilateral hemispheres (n=3). np<0.05 vs contralateral hemispheres from control (HIF-1αF/F) mice. #p<0.05 vs ipsilateral hemispheres from control (HIF-1αF/F) mice. (D) Representative TTC staining images of brain sections of MCAO mice. The brains were sectioned from the 6-mm position from the frontal pole. (E) Quantification of infarct volume estimated from TTC-stained sections (n=3). Values are means±SEM, np<0.05 vs control (HIF-1αF/F) mice.