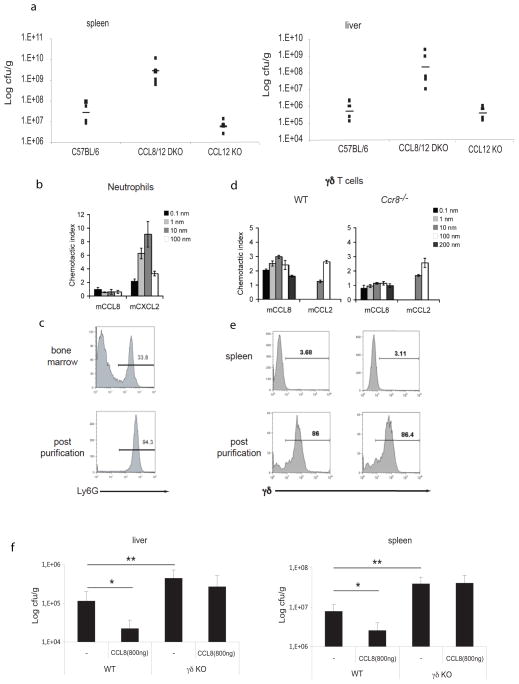
Figure 7. γ/δ T cells are the cellular target of CCL8 chemotactic activity.
a, L. monocytogenes in vivo infection was performed in six different Ccl8/12 DKO or six Ccl12 single KO mice. Six sex and age-matched C57BL/6 mice were used as controls. Infected spleens and livers were harvested 48 hpi and bacterial loads calculated. Data represent means ± SD. *p=0.001 (two-tailed Student’s t-test). b. Neutrophils purified from the bone marrow of WT mice were assayed for migration to mCCL8 and the positive control mCXCL2 in a Neuroprobe chemotaxis chamber. c. Purity of neutrophils determined by Ly6G staining. d. γ/δ T cells isolated from WT and Ccr8 −/− mouse spleens were assayed for migration to mCCL8 and the positive control mCCL2 in a Neuroprobe chemotaxis chamber. e. Purity of WT and Ccr8 −/− γ/δ T cells determined by γ/δ TcR staining. Data in b–e are representative of three independent experiments. f, L. monocytogenes in vivo infection was performed in γ/δ T cell KO or C57BL/6 WT mice that had received CCL8 i. v. Infected spleens and livers were harvested 48 hpi and bacterial loads calculated. Data are from 2 different experiments conducted separately. P-values were calculated by two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p<0.001 untreated versus CCL8-treated WT mice; *p<0.05 untreated WT versus untreated γδ KO mice.