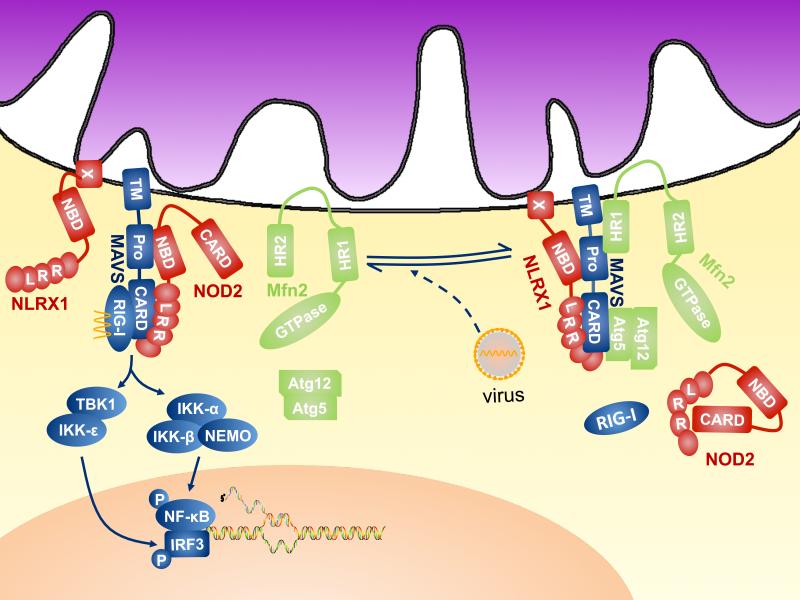
Fig. 2.
NLR proteins and regulation of the mito-signalosome. In the quiescent state (Complex A), the CARD:CARD homotypic interaction between MAVS and RIG-I is prevented by MAVS association with NLRX1, Atg5-Atg12 conjugate, perhaps by steric hindrance. Mfn2 interacts with the C-terminus and the transmembrane region of MAVS to abolish its immune-activating function. The three regulatory proteins target different regions of MAVS to execute the “molecular brake”. In the presence of cytosolic 5'-triphosphate single stranded RNA or double stranded RNA, these brakes are released, which renders the assembly of the active form of mitosignalosome (Complex B), in which MAVS interacts with NOD2 and RLRs, such as RIG-I, which directly interact with viral nucleic acid to trigger type I IFN production.