Figure 7. Mecp2 occupancy at the Avp enhancer coupled with repressive chromatin marks and repressor complexes.
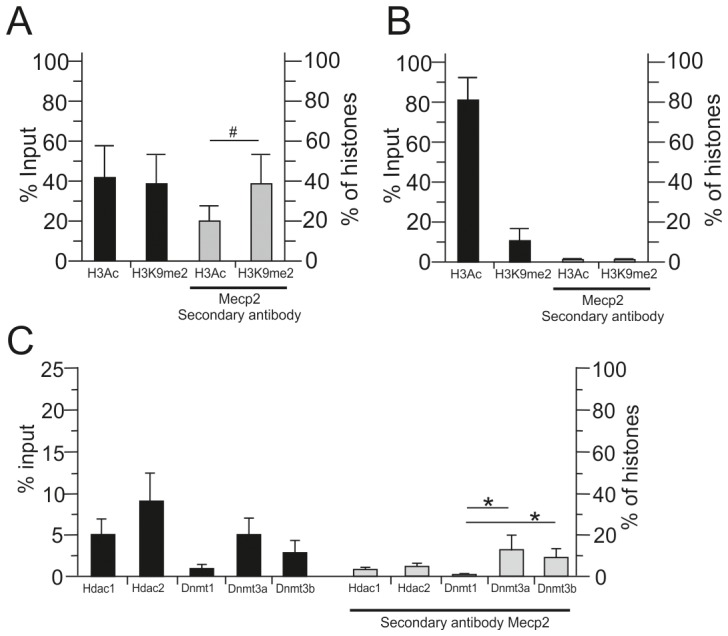
A, Chromatin samples from the PVN were subjected to seqChIP. The first ChIP was done with antibodies against H3Ac (panacetylated-histone H3), an active mark, and H3K9me2 (dimethyl-histone H3, Lys-9), a repressive mark. The second round ChIP was carried out with anti-Mecp2. Hereby, Mecp2 was preferentially, with a distinct trend toward significance, contained in the chromatin fraction associated with the transcriptionally inactive Avp enhancer. B, PVN tissues from Mecp2 null male (-/y) mice showed increased H3Ac and decreased H3K9me2 chromatin marks at the Avp enhancer compatible with a repressor function of Mecp2. However, due to the knockout of Mecp2, the anti-Mecp2 antibody did not enrich for either chromatin fraction attesting to its specificity. C, Sequential ChIP experiments showed that Mecp2 occupancy at the ELS-responsive enhancer associated with the chromatin fraction containing Hdacs and Dnmts. Chromatin samples from hypothalamus were immunoprecipitated in the first ChIP experiment with antibodies against Hdac1, Hdac2, Dnmt1, Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b. Following on two-thirds of the product of the primary ChIP were precipitated in the second ChIP with anti-C-terminal Mecp2; the remaining sample was used for the analysis of the primary ChIP. DNA recovered from both ChIP steps was analyzed by qPCR for the presence of the Avp enhancer. Bars represent standard deviations from the mean (sem), *, P<0.05; #, P<0.07 from 5 independent experiments performed.
