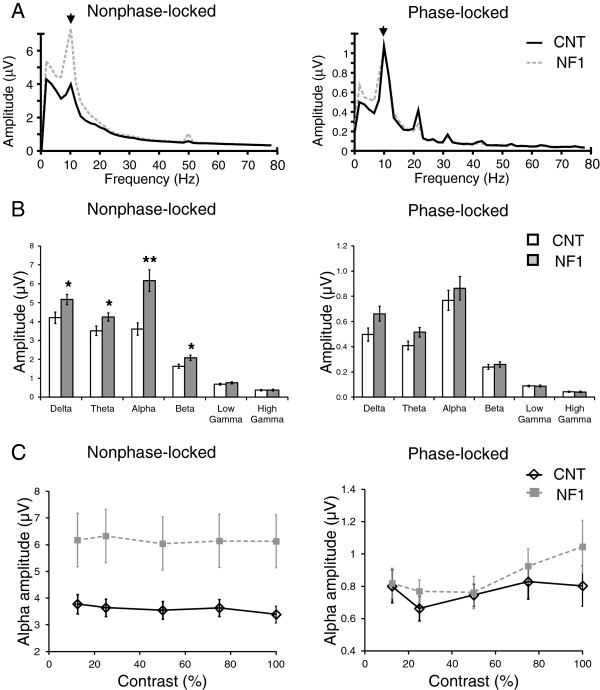
Figure 5.
Frequency domain analysis of the electroencephalographic (EEG) responses elicited by achromatic stimulation revealed significantly higher non-phase-locked alpha amplitude in children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). (A) Grand average amplitude spectra of neural oscillations non-phase-locked (left) and phase-locked (right) with the visual stimulation. (B) Control and NF1 average amplitude of each frequency band (theta, alpha, beta, low gamma and high gamma) for non-phase-locked (left) and phase-locked (right) oscillations. (C) Mean amplitude of non-phase-locked (left) and phase-locked (right) alpha as a function of stimulus contrast. All data are represented as mean ± 1 standard error of the mean. *P <0.05; **P <0.01.