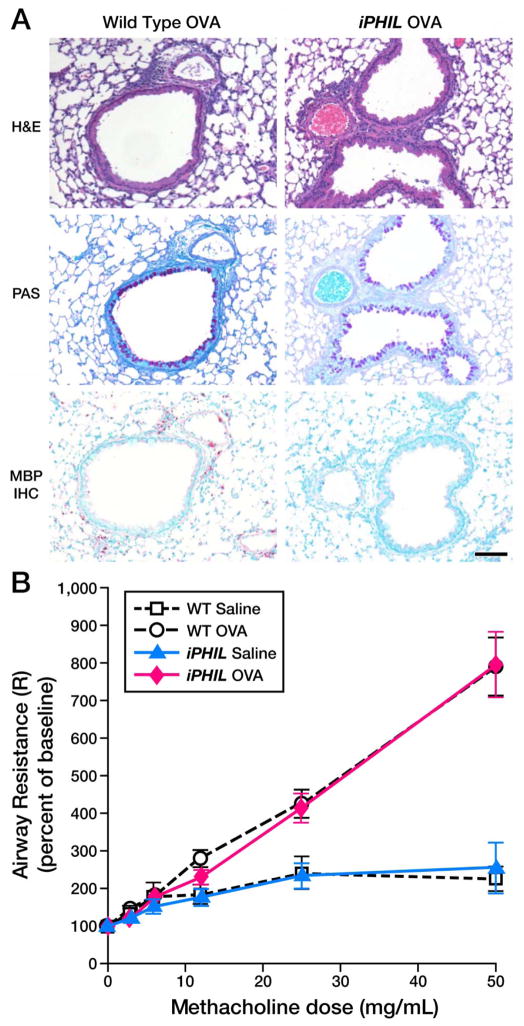
Figure 4. iPHIL mice rendered eosinophil-deficient during the OVA airway challenge phase displayed allergen-induced pulmonary histopathologies and lung dysfunction equivalent to OVA-treated wild type animals.
(A) Representative photomicrographs of lung sections are presented from wild type as compared iPHIL mice whose eosinophils were ablated exclusively during the airway challenge phase of the OVA provocation protocol outlined earlier (see Figure 3(D)). Lung sections were stained with H&E and PAS as well as immunohistochemistry for the identification of infiltrating eosinophils (MBP-IHC). These data demonstrated that the lungs of iPHIL mice rendered eosinophil deficient during airway OVA challenge (iPHIL OVA) displayed equivalent levels (relative to OVA-treated wild type controls (Wild Type OVA)) of airway epithelial hypertrophy (H&E), goblet cell metaplasia/airway epithelial cell mucin accumulation ((PAS) – dark purple staining cells)) despite the lack of eosinophils (MBP IHC – red staining cells infiltrating the parenchyma). Scale bar = 100μm. (B) OVA-treated wild type and iPHIL mice rendered eosinophil-deficient during the airway challenge phase of the OVA provocation protocol displayed equivalent levels of airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) relative to saline-treated control groups. *P<0.05.