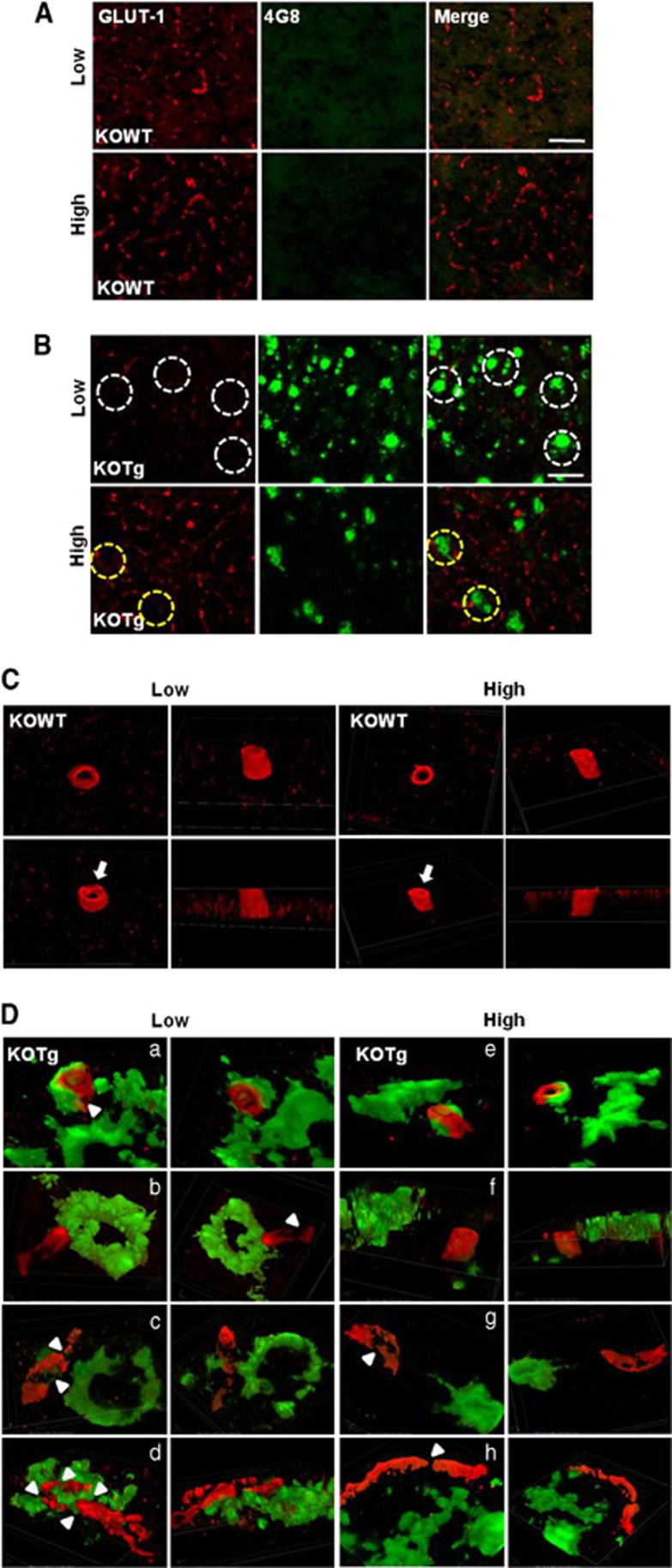
Figure 2.
Cerebral capillaries are less impaired in the brains from the high-supplementation group of 5XFAD mice. (A) Coronal serial sections of brains from 6-month-old mice (n=4 for each from standard and decreased groups) were co-immunostained with anti-GLUT1 (red) and anti-Aβ (green; 4G8) antibodies and imaged by confocal microscopy. Capillaries stained with anti-GLUT1 antibody (red) showed long tubular-like form in KO-WT mice of both treatment groups. (B) KO-Tg mice displayed amyloid plaque deposition (green) and cut capillary forms. Capillaries adjacent to the amyloid plaques displayed disconnected tubular-like form in KO-Tg mice (shown in the yellow dotted circle). Decreased impairment was observed in the high-dose supplemented KO-Tg mice than the low-dose supplemented KO-Tg mice (shown in the white dotted circle). Scale bar=50 μm. (C) 3D-SIM images of the brains from the KO-WT mice in both treated groups. (D) 3D-SIM images of the brains from both the low-dose supplemented KO-Tg (a–d) and the high-dose supplemented KO-Tg mice (e–h). Brain slices were recorded on 3D-SIM images along z axis with a thickness of 0.15 μm, reconstructed and 3D volume images were created with the alpha blending function. Axial directions are represented on each image. Capillaries stained with anti-GLUT1 antibody (red) and amyloid plaque stained with anti-Aβ (green; 4G8) antibody. Arrow, sectioned z axis image; arrow head, damaged micro-vessel. Scale bars=2 μm. 3D depth, 2.8–4.5 μm in the high-dose supplemented KO-Tg and 3.9–7.6 μm in the low-dose supplemented KO-Tg mice