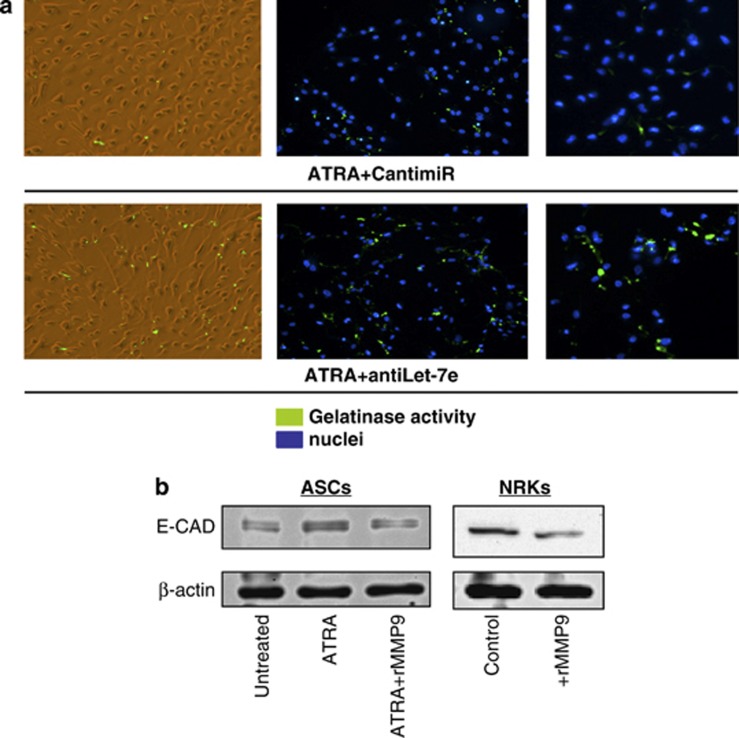
Figure 7.
MMP9 is involved in ASC differentiation with ATRA. (a) In situ zymography for MMP9. The left column panel shows the increased gelatinolytic activity in ASCs cultured with ATRA and silenced at day 4 with 100 nM antiLet-7e (ATRA+antiLet-7e) with respect to ASCs transfected with a control oligonucleotide (ATRA+CantimiR). The middle column panel indicates the results obtained when ASCs were incubated for 1 h with FITC-labeled DQ-gelatin. Green dots represent gelatinolytic activity of cultured cells. Results show an increase in gelatinolytic activity in silenced cells (ATRA+antiLet-7e). Magnification × 20 (middle panel). Magnification × 40 (right panel). A negative control was included by incubating the cells with 20 mM EDTA. (b) In two different kinds of epithelial cells, epithelial differentiated ASCs (left panel) and in renal epithelial cell line NRK-52e after addition of recombinant MMP9 (2 μg/ml and incubated for 72 h), western blot analysis of E-cadherin indicates a reduction in E-cadherin protein expression after MMP9 addition in the two cell lines. Equal loading was controlled by β-actin expression. A representative picture from four experiments is shown. ASCs treated with ATRA showed a significant increase in E-cadherin expression compared with untreated cells. This increase could be blocked by the addition of recombinant MMP9 (ATRA+MMP9). Addition of recombinant MMP9 to ASCs (ATRA+MMP9) or NRK cells (+MMP9) decreased E-cadherin expression