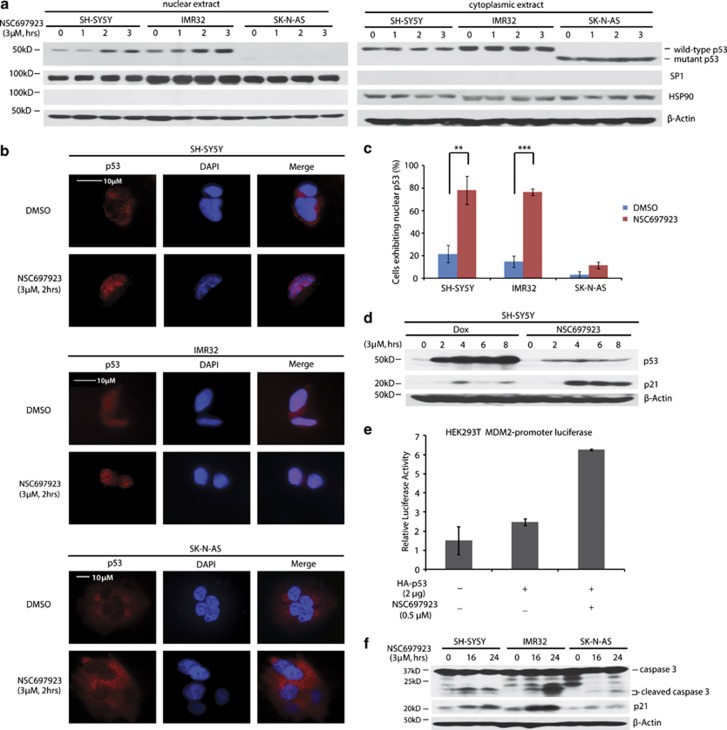
Figure 3.
NSC697923 induces apoptosis by activation of p53 in p53 wild-type NB cells. (a) SH-SY5Y, IMR32, and SK-N-AS cells were treated with indicated concentrations of NSC697923 for different time courses, after which cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were extracted, subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with p53 antibodies. The purity of nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts was proved by anti-SP1 and anti-HSP90, respectively. (b and c) SH-SY5Y, IMR32, and SK-N-AS cells were incubated with or without 3 μM of NSC697923 for 2 h, cells were then fixed, incubated with anti-p53 antibodies, and then with Alexa Fluor 555 goat anti-mouse. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI. Then images were acquired, and the number of cells exhibiting nuclear p53 before and after NSC697923 treatment was counted and represented as mean±S.D. P-values <0.01 (**) or <0.001 (***) were indicated. (d) SH-SY5Y cells were treated with 3 μM of NSC697923 or Dox for the time courses as indicated and immunoblotted with p53 and p21 antibodies. Beta-actin was detected as a loading control. (e) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with MDM2 promoter-luciferase reporter plasmid and Renilla-luciferase control plasmid along with Topo-HA-p53 or Topo-vector plasmid. After 48 h, cells were either left untreated or treated with 0.5 μM of NSC697923 for 16 h. The relative MDM2-luciferase activity was determined by dividing the firefly luciferase activity by Renilla luciferase activity. (f) SH-SY5Y, IMR32, and SK-N-AS cells were treated with 2 μM of NSC697923 for the time courses as indicated and immunoblotted with caspase 3 and p21 antibodies. Beta-actin was detected as a loading control. Data from a and f are representative of three independent experiments. Data from b to e are representative of two independent experiments