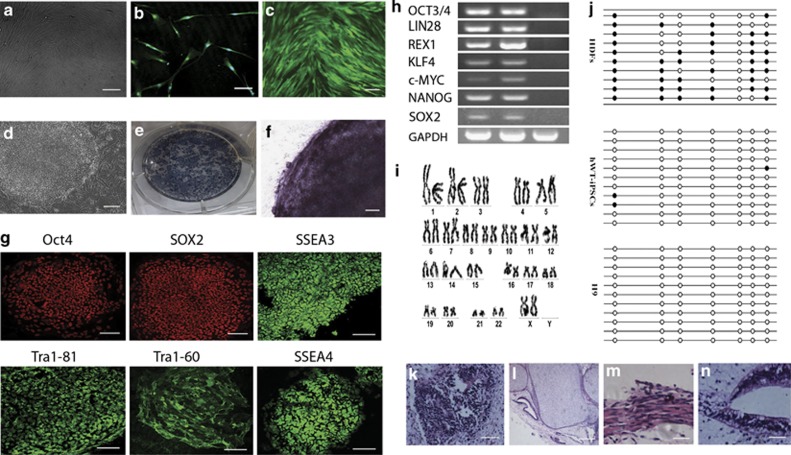
Figure 1.
Characterization of human dermal fibroblasts used for hiPSC induction. (a) Culture of human dermal fibroblasts (bar=50 μm). (b) TE-7 immunostaining confirmed that the resulting cultures were of fibroblast identity (bar=100 μm). (c) Phase contrast image of human dermal fibroblasts transfected with GFP retroviruses (bar=100 μm). (d) The hESC-like hiPS colony (bar=50 μm). (e and f) These hESC-like colonies showed high alkaline phosphatase expression (bar=50 μm). (g) Immunocytofluorescence of the hiPSCs showing the expression of multiple hESC markers (bar=100 μm). (h) RT-PCR analysis of hESC marker genes in hiPSCs. (i) No karyotypic abnormalities were observed in the hiPSCs. (j) Open circles indicate unmethylated CpG dinucleotides, whereas closed circles indicate methylated CpGs in the promotor of Oct4. After transplantation into the hind limb muscle of NOD/SCID mice, hiPSCs generated teratomas showing (k) neural tissue (ectoderm; bar=100 μm), (l) cartilage (mesoderm; bar=100 μm), (m) muscle (mesoderm; bar=100 μm) and (n) primitive gut (endoderm; bar=100 μm)