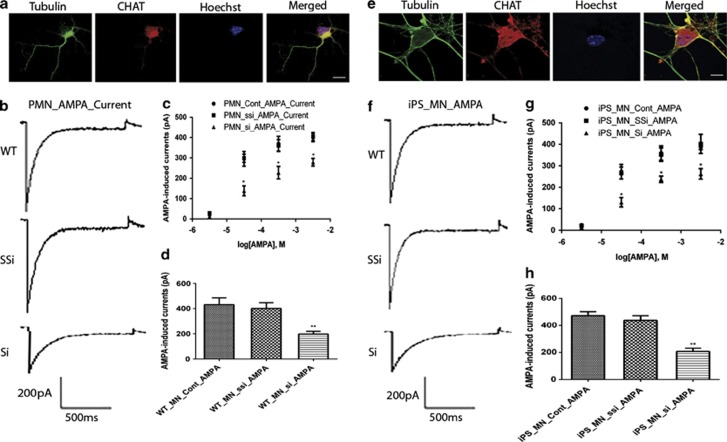
Figure 5.
PTEN knockdown decreases AMPA-induced whole-cell currents in primary cultured (a–d) and iPS-derived (e–h) motor neurons. Primary cultured (a) and iPS-derived (e) motor neurons were immunostained with anti-tubulin (green), Hoechst (nuclear staining in blue) and ChAT (red). Scale bar, 20 μm. (b and f) Representative current traces elicited by AMPA. (c and g) Dose response of AMPA-induced whole-cell currents were recorded in 20 mM extracellular Na+ at −60 mV, in response to AMPA concentrations ranging from 5 μM to 5 mM. Each point represents the mean±S.E.M. from three cells (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, tested by one-way ANOVA). EC50 values estimated from fits to pooled data were 106 μM for primary cultured motor neurons and 113 μM for iPS-derived neurons. (d and h) Average peak AMPA-induced whole-cell currents were recorded in Na+-free extracellular solution containing 50 mM Ca2+ at −60 mV in primary cultured and iPS-derived motor neurons, evoked by AMPA 100 μM (n=8). Columns represent the peak amplitudes of agonist-induced whole-cell currents. Results represent the mean+S.E.M. from four independent experiments, with 8 motor neurons of each (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, tested by one-way ANOVA)