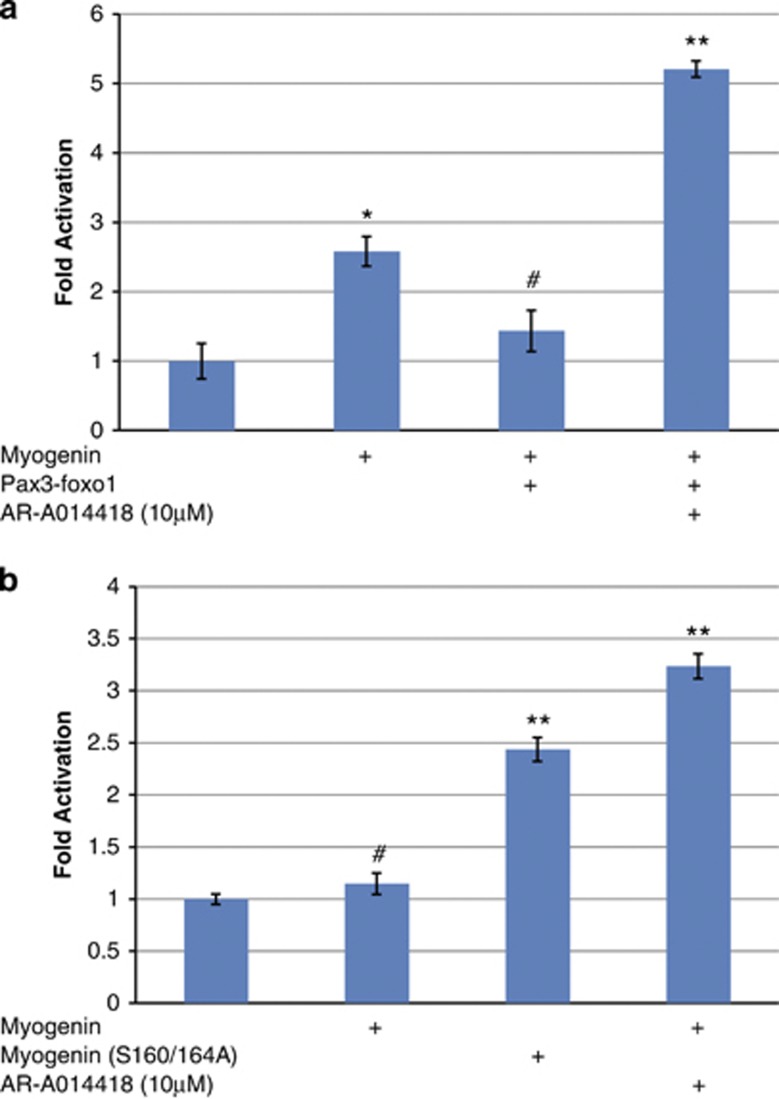
Figure 5.
Pharmacological inhibition of GSK3β rescues PAX3-FOXO1 repression of MYOGENIN's transcriptional activation of MCK promoter in both C2C12 myoblasts and RH30 human ARMS cells. (a) MCK-Luc promoter activity was assessed in C2C12 myoblasts that were transfected with different combinations of MYOGENIN, PAX3-FOXO1 and pcDNA3.1 control plasmid as indicated and then treated with either 10 μM AR-A014418 or DMSO solvent. MYOGENIN enhanced MCK-Luc activity as expected (P<0.001) and this effect was repressed by co-expression of PAX3-FOXO1 (P<0.01). Pharmacological inhibition of GSK3β not only reversed the effect of PAX3-FOXO1 but resulted in a super-activation (P<0.001). (b) To assess the importance of these findings in human-derived ARMS, RH30 cells were transfected with either MYOGENIN or mutated MYOGENIN(S160/164A) and MCK-Luc promoter activity was assessed. The data shows that wild-type MYOGENIN could not trans-activate the MCK promoter region unless it was coupled with pharmacological inhibition of GSK3β (P<0.001). This was in contrast to mutated MYOGENIN (S160/164A), which could potentiate MCK promoter activity (P<0.001) regardless of GSK3β inhibition. (c) Summary of our findings: GSK3β activity in ARMS represses the activation of muscle-specific genes by repressing the transcriptional activity of MYOGENIN. #ns, *P<0.01, **P<0.001