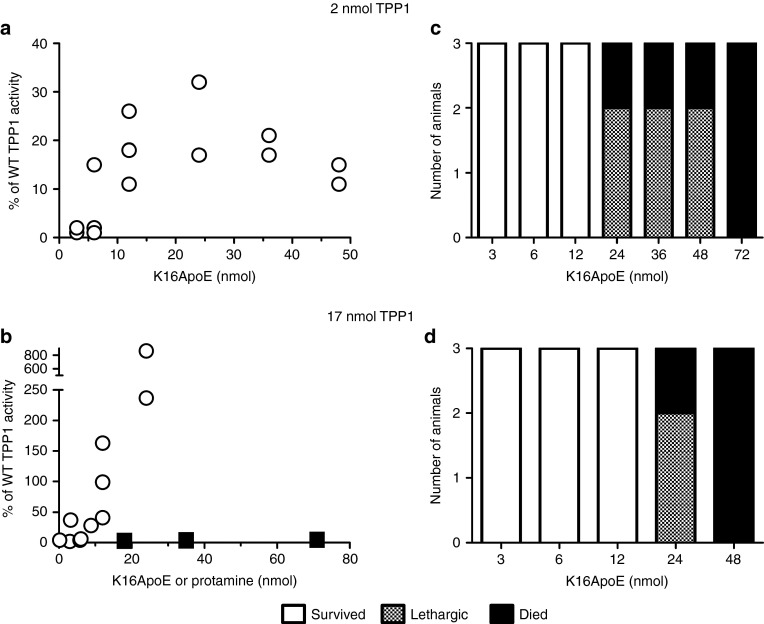
Figure 1.
Dose-response analysis of K16ApoE and tripeptidyl peptidase I (TPP1) mixtures. Six-week-old late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (LINCL) mice were administered a 120 µl bolus dose of a mixture of the indicated amount of TPP1 and either K16ApoE (circles) or protamine sulfate (filled squares). (a,b) Delivery of TPP1 to the brain. Mice were killed 24 hours after injection and TPP1 activity was assayed in brain. Results were expressed as the percentage of wild-type specific activity after correction for background using untreated LINCL mice. (c,d) Response of animals after administration of indicated dose of TPP1 and K16ApoE was plotted. Note that acute treatment of LINCL mice with 42 nmol K16ApoE in the absence of TPP1 resulted in death (n = 4). Mice administered protamine sulfate did not exhibit any adverse effects.