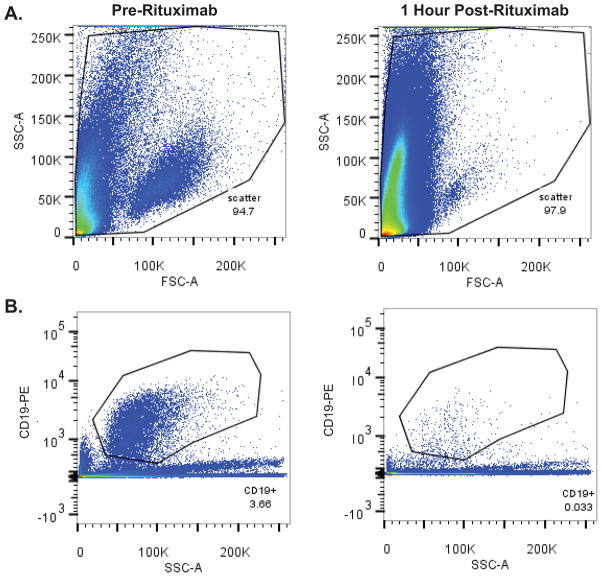
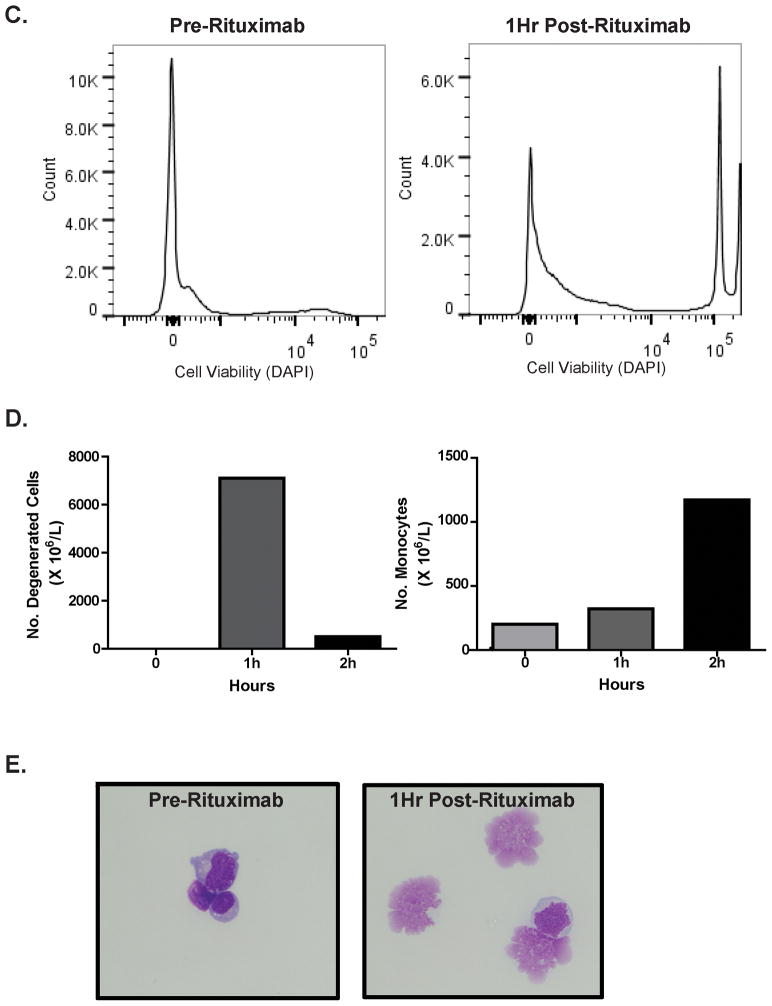
Figure 1. Rapid lymphocytotoxic effects within the CSF following intraventricular rituximab.
Figure 1A. Forward versus side scatter FACS plots of CSF cells from a subject with recurrent CNS lymphoma, pre (left) and 1 hour post (right) intraventricular rituximab monotherapy treatment. (3 ml CSF analyzed/condition).
Figure 1B. Anti-CD19 (PE-labeled)-positive populations in the CSF pre (left) and 1 hour post (right) intraventricular rituximab in same patient as in 1A.
Figure 1C. Intra-CSF cell toxicity assessment pre (left) and 1 hour post (right) intraventricular rituximab in a different patient treated with rituximab monotherapy, measured by DAPI positivity, which demonstrated a rapid increase in the number of DAPI+ non-viable cells. The increased number of DAPI+ cells also correlated with a marked decrease in CD19+ B-cells within CSF.
Figure 1D. Degenerated cell quantification (as reported by the UCSF Clinical Laboratory) in CSF of a third subject with recurrent CNS lymphoma, at baseline, 1 hour and 2 hours post-treatment with intraventricular rituximab. Rituximab was associated with a time-dependent increase in CSF monocytosis during this interval.
Figure 1E. Cytologic appearance of malignant cells in CSF at baseline (left), and degenerated cells one hour after intraventricular rituximab (right). (X 400).