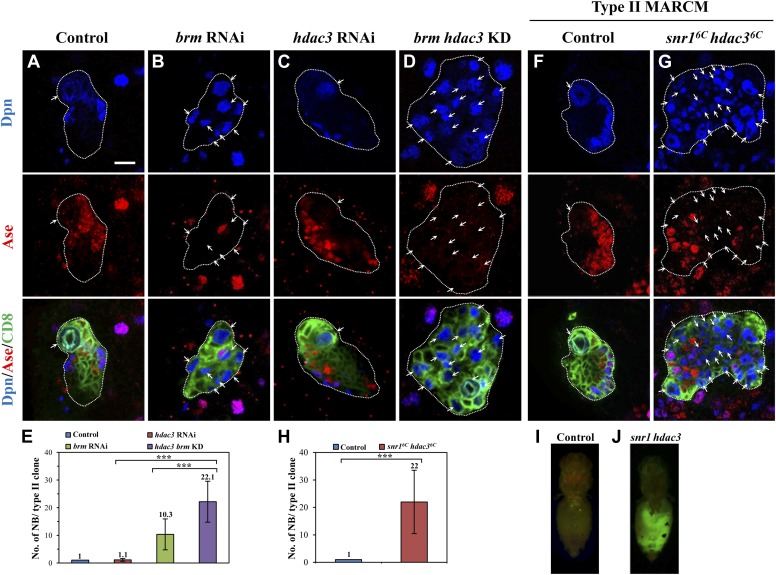
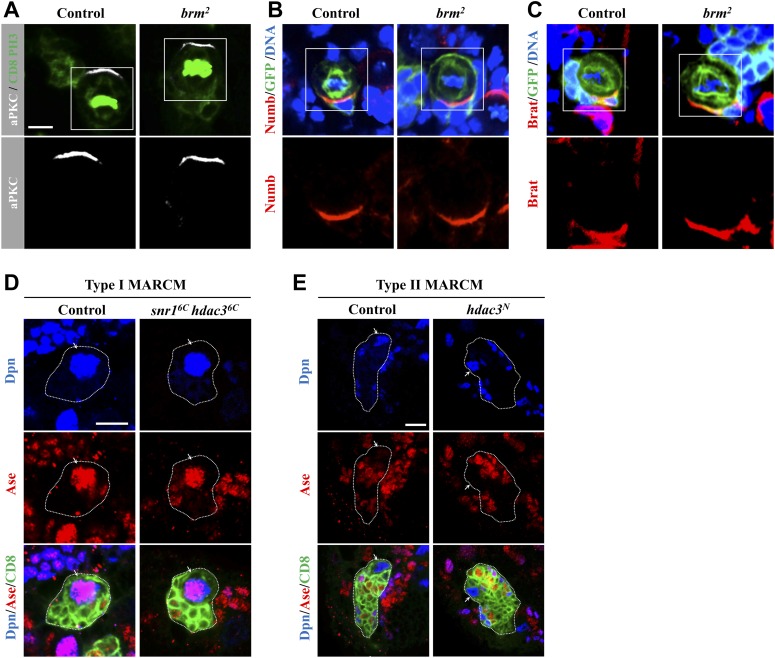
Figure 3. HDAC3 acts cooperatively with the Brm complex to suppress the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts.
(A–D) The driver control (A), brm RNAi (B), hdac3 RNAi (C), brm hdac3 double knockdown (D) under the type II driver were labeled with Dpn, Ase, and CD8. (E) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone in A–D. (F–G) Type II MARCM clones from the driver control (F) and snr16c hdac36c (G) homozygous MARCM clones were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. Arrows indicate neuroblasts. (H) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone in F–G. *** indicates p<0.001. (I–J) Clones are marked by CD8::GFP and indicated by white dotted line. Larval brain tissues from the wild-type MARCM clones (I) and snr16c hdac36c MARCM clones (J) were implanted into the abdomen of wild-type hosts. Scale bar, 10 µm.