Figure 6.
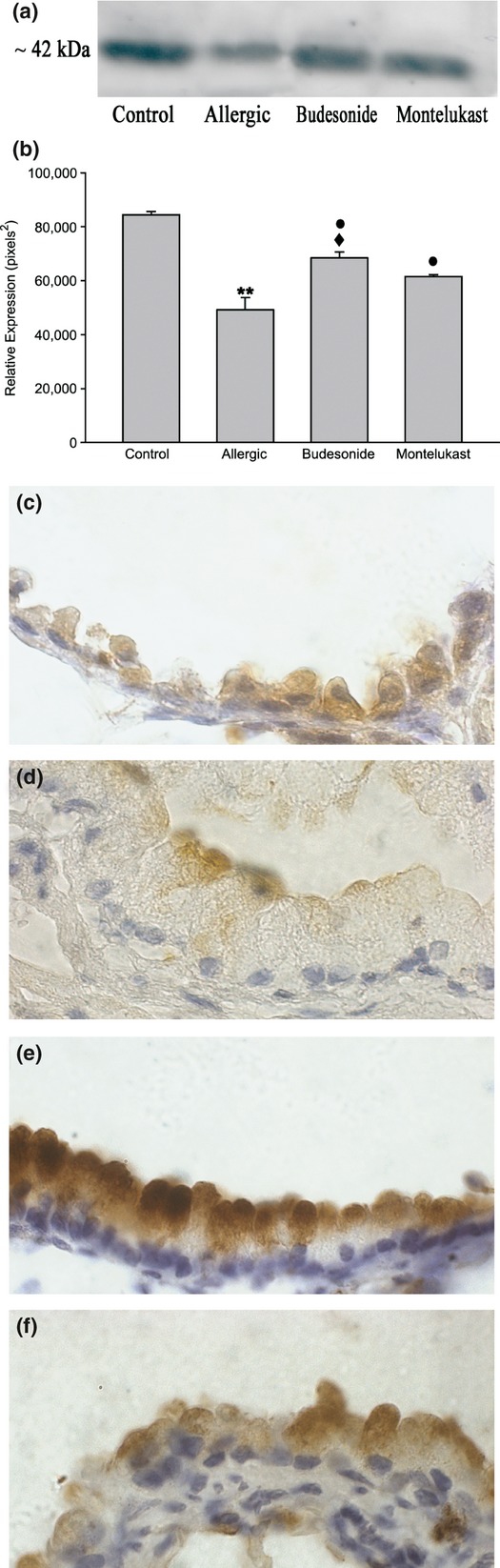
Analysis of SP-D content in chronic allergy: Western blot analysis (6a and b) and paraffin sections immunolabelled with anti-SP-D antibody followed by peroxidase-DAB (c–f). By Western blot, a significant reduction in SP-D in lung homogenate was noted in comparison with control (**P < 0.05), with both anti-inflammatory treatments inducing a marked increase compared with allergic values (•P < 0.05). By immunohistochemistry, normal Clara cells exhibited SP-D label in the whole cytoplasm, which was stronger delineating the plasma membrane (b); the hypertrophied mucous cells induced by chronic allergy expressed scarce SP-D content restricted to the apical portion under the plasma membrane (c). Budesonide (BUD) and montelukast (MK) anti-inflammatory treatments increased the antimicrobial content (d and e), which appeared to be particularly intense after BUD treatment (♦P < 0.05) (d). Bar represents 20 μm.
