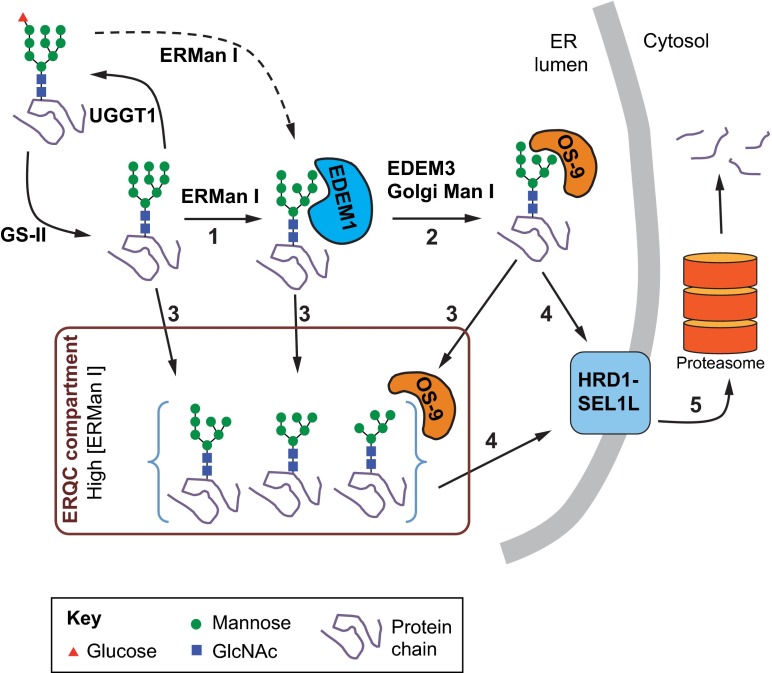
Fig. 3.
Glycoprotein ERAD. Degradation of terminally misfolded glycoproteins through ERAD is probably initiated by cleavage of the terminal B-chain mannose (green circles) of Man9GlcNAc2 (and possibly Glc1Man9GlcNAc2) N-glycan forms by ER mannosidase I (ERManI, step 1). This results in the formation and recognition of this specific Man8GlcNAc2 form by ER-degradation-enhancing alpha-mannosidase-like 1 (EDEM1). Then, removal of the terminal C-chain mannose, either: (1) directly by EDEM3 or possibly Golgi mannosidase I (step 2), or (2) by highly concentrated ERMan I in the ERQC compartment (step 3), exposes an α1-6 linked mannose that is recognized by OS-9. OS-9 facilitates transport of the misfolded substrate to the core ERAD HRD1-SEL1L complex (step 4), and subsequent retrotranslocation to the cytoplasm for degradation by the proteasome (step 5).