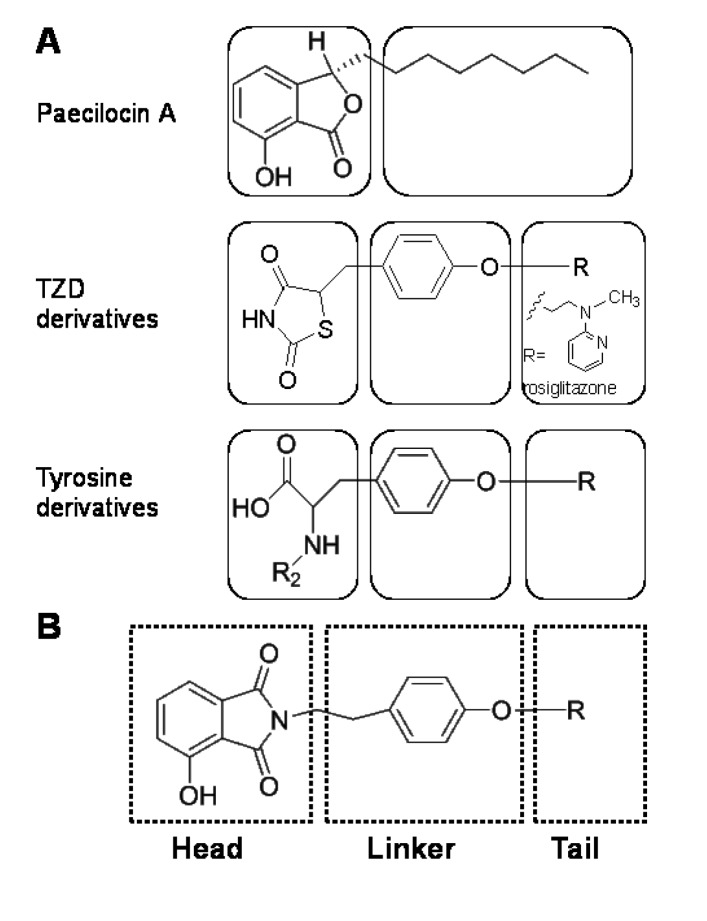
Figure 1.
(A) Simplified topologies of paecilocin A and typical synthetic PPAR-γ agonists. Paecilocin A contains a hydrophilic 3-hydroxy phthalide moiety and a hydrophobic octyl chain; both thiazolidinedione (TZD) and tyrosine derivatives employ a phenol moiety as a linker between their hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails. (B) The N-substituted phthalimide skeleton of PPAR-γ agonists; a 3-hydroxy phthalimide moiety acts as the head, a phenol moiety as the central linker and a hydrophobic or hydrophilic substituent as the tail.