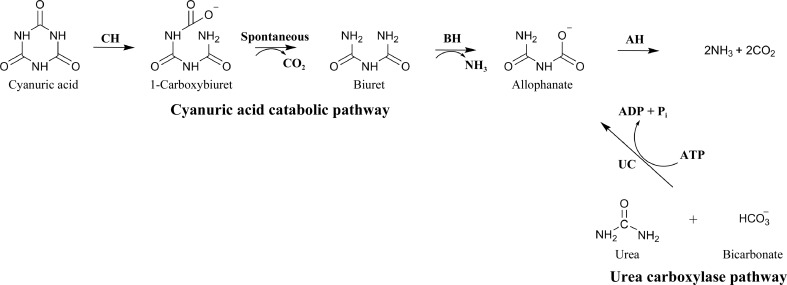
Figure 1.
Catabolic processes involving allophanate hydrolase (AH). The cyanuric acid catabolic pathway involves ring opening of cyanuric acid by cyanuric acid hydrolase (CH), spontaneous decarboxylation of the product (1-carboxybiuret) and deamination of biuret by biuret hydrolase (BH) to produce allophanate. The urea catabolic pathway involves ATP-dependent urea carboxylation by urea carboxylase (UC) to produce allophanate. Both pathways then depend upon allophanate deamination by allophanate hydrolase to avoid spontaneous decarboxylation (and urea formation).