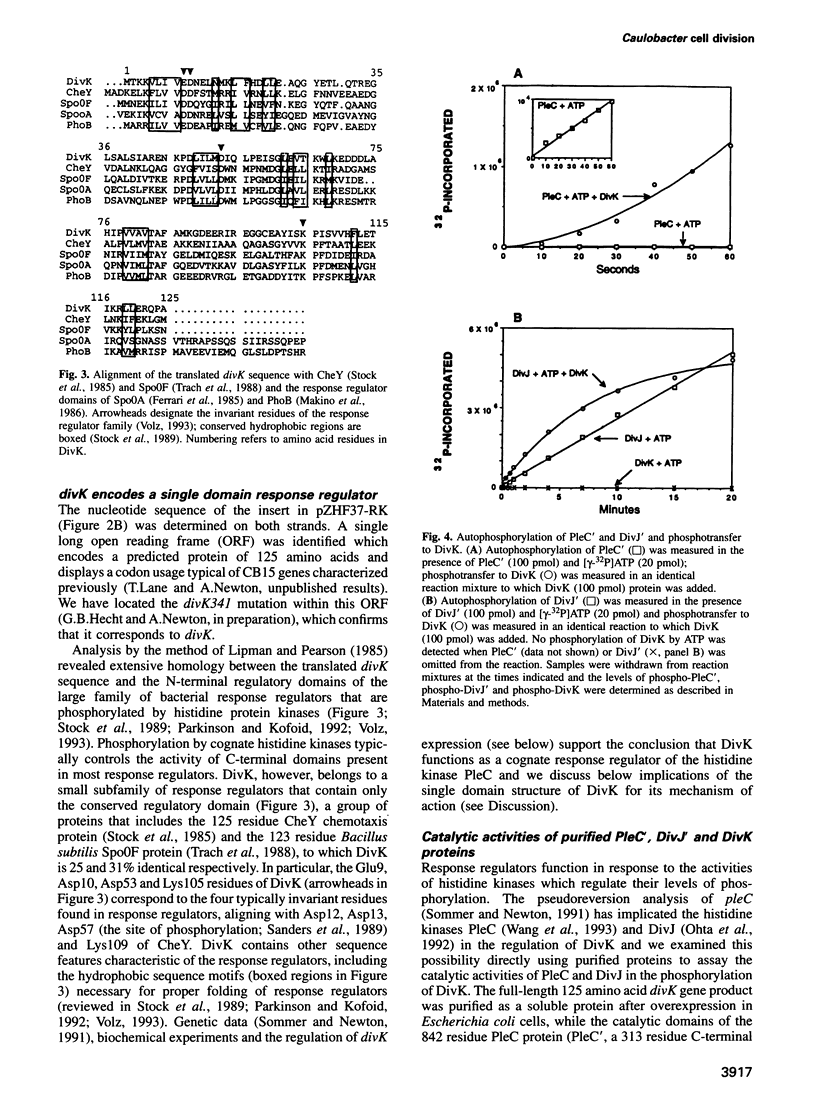
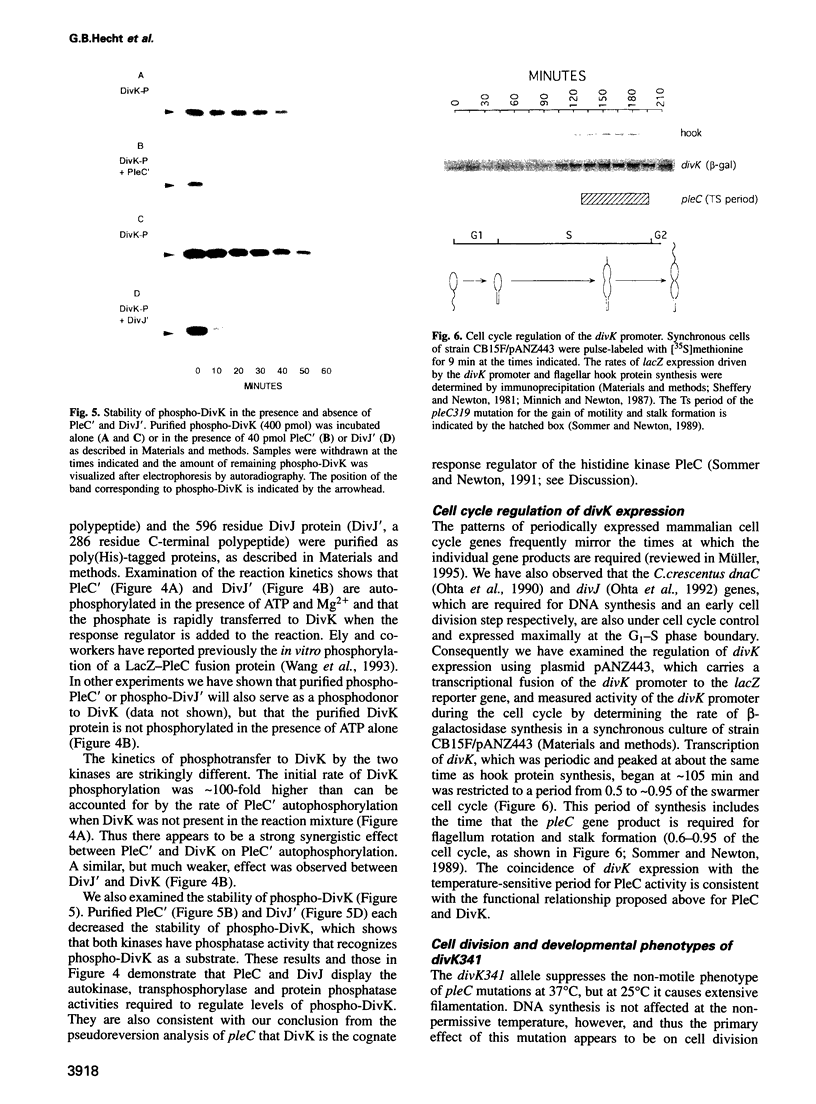
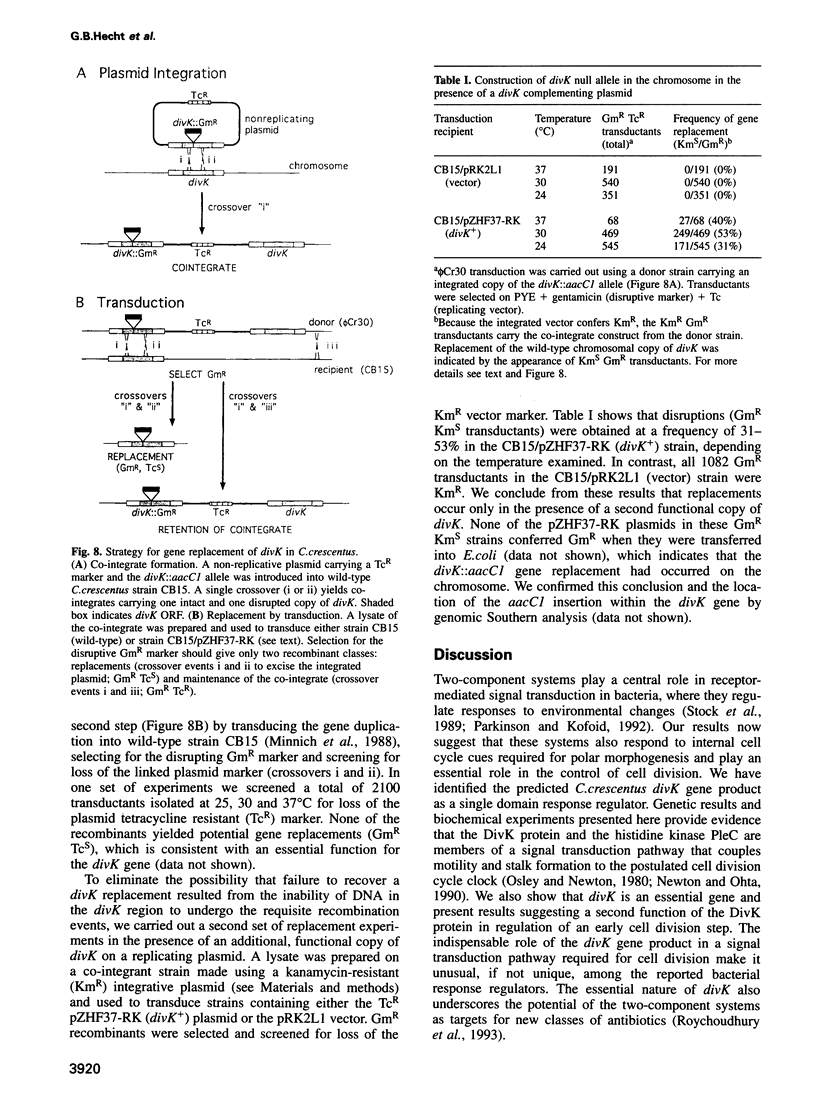
Abstract
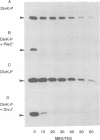
Signal transduction pathways mediated by sensor histidine kinases and cognate response regulators control a variety of physiological processes in response to environmental conditions. Here we show that in Caulobacter crescentus these systems also play essential roles in the regulation of polar morphogenesis and cell division. Previous studies have implicated histidine kinase genes pleC and divJ in the regulation of these developmental events. We now report that divK encodes an essential, cell cycle-regulated homolog of the CheY/Spo0F subfamily and present evidence that this protein is a cognate response regulator of the histidine kinase PleC. The purified kinase domain of PleC, like that of DivJ, can serve as an efficient phosphodonor to DivK and as a phospho-DivK phosphatase. Based on these and earlier genetic results we propose that PleC and DivK are members of a signal transduction pathway that couples motility and stalk formation to completion of a late cell division cycle event. Gene disruption experiments and the filamentous phenotype of the conditional divK341 mutant reveal that DivK also functions in an essential signal transduction pathway required for cell division, apparently in response to another histidine kinase. We suggest that phosphotransfer mediated by these two-component signal transduction systems may represent a general mechanism regulating cell differentiation and cell division in response to successive cell cycle checkpoints.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson A. K., Ramakrishnan G., Ohta N., Feng J., Ninfa A. J., Newton A. The Caulobacter crescentus FlbD protein acts at ftr sequence elements both to activate and to repress transcription of cell cycle-regulated flagellar genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4989–4993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y. V., Marczynski G., Shapiro L. The expression of asymmetry during Caulobacter cell differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:419–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbulys D., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90238-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Kwok S. F., Bleecker A. B., Meyerowitz E. M. Arabidopsis ethylene-response gene ETR1: similarity of product to two-component regulators. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.8211181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari F. A., Trach K., LeCoq D., Spence J., Ferrari E., Hoch J. A. Characterization of the spo0A locus and its deduced product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2647–2651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochuli E., Döbeli H., Schacher A. New metal chelate adsorbent selective for proteins and peptides containing neighbouring histidine residues. J Chromatogr. 1987 Dec 18;411:177–184. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93969-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvitz H. R., Herskowitz I. Mechanisms of asymmetric cell division: two Bs or not two Bs, that is the question. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):237–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90468-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huguenel E. D., Newton A. Localization of surface structures during procaryotic differentiation: role of cell division in Caulobacter crescentus. Differentiation. 1982;21(2):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaka H., Armfield A. Y., Lombard G. L., Dowell V. R., Jr Practical procedure for demonstrating bacterial flagella. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):948–952. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.948-952.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacker M. G., Newton A. Information essential for cell-cycle-dependent secretion of the 591-residue Caulobacter hook protein is confined to a 21-amino-acid sequence near the N-terminus. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Oct;14(1):73–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll D. J., Abdel-Malek Abdel-Hafiz H., Marcell T., Simpson S., Chen C. Y., Gutierrez-Hartmann A., Lustbader J. W., Hoeffler J. P. A multifunctional prokaryotic protein expression system: overproduction, affinity purification, and selective detection. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;12(5):441–453. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDeaux J. R., Grossman A. D. Isolation and characterization of kinC, a gene that encodes a sensor kinase homologous to the sporulation sensor kinases KinA and KinB in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1995 Jan;177(1):166–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.1.166-175.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Murray A. W. Feedback control of mitosis in budding yeast. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):519–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukat G. S., Stock J. B. Response regulation in bacterial chemotaxis. J Cell Biochem. 1993 Jan;51(1):41–46. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240510109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Wurgler-Murphy S. M., Saito H. A two-component system that regulates an osmosensing MAP kinase cascade in yeast. Nature. 1994 May 19;369(6477):242–245. doi: 10.1038/369242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide sequence of the phoB gene, the positive regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 5;190(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleary W. R., Zusman D. R. Purification and characterization of the Myxococcus xanthus FrzE protein shows that it has autophosphorylation activity. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6661–6668. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6661-6668.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnich S. A., Newton A. Promoter mapping and cell cycle regulation of flagellin gene transcription in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1142–1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minnich S. A., Ohta N., Taylor N., Newton A. Role of the 25-, 27-, and 29-kilodalton flagellins in Caulobacter crescentus cell motility: method for construction of deletion and Tn5 insertion mutants by gene replacement. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3953–3960. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3953-3960.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R. Transcriptional regulation during the mammalian cell cycle. Trends Genet. 1995 May;11(5):173–178. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(00)89039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A., Ohta N. Regulation of the cell division cycle and differentiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:689–719. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Ninfa E. G., Lupas A. N., Stock A., Magasanik B., Stock J. Crosstalk between bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction proteins and regulators of transcription of the Ntr regulon: evidence that nitrogen assimilation and chemotaxis are controlled by a common phosphotransfer mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5492–5496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Hynes R. H., Bender R. A. Recombination deficient mutant of Caulobacter crescentus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(2):275–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00383006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Chen L. S., Mullin D. A., Newton A. Timing of flagellar gene expression in the Caulobacter cell cycle is determined by a transcriptional cascade of positive regulatory genes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1514–1522. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1514-1522.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
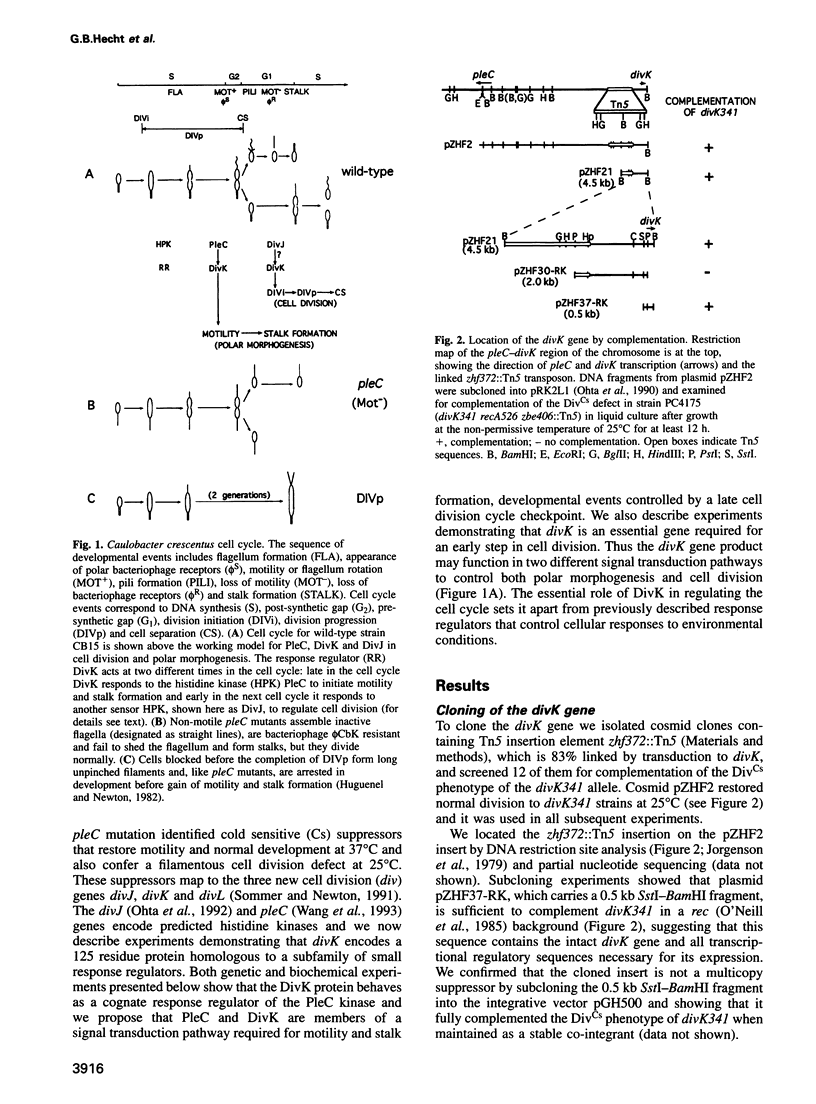
- Ohta N., Lane T., Ninfa E. G., Sommer J. M., Newton A. A histidine protein kinase homologue required for regulation of bacterial cell division and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10297–10301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Masurekar M., Newton A. Cloning and cell cycle-dependent expression of DNA replication gene dnaC from Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7027–7034. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7027-7034.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Swanson E., Ely B., Newton A. Physical mapping and complementation analysis of transposon Tn5 mutations in Caulobacter crescentus: organization of transcriptional units in the hook gene cluster. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):897–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.897-904.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Newton A. Temporal control of the cell cycle in Caulobacter crescentus: roles of DNA chain elongation and completion. J Mol Biol. 1980 Mar 25;138(1):109–128. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota I. M., Varshavsky A. A yeast protein similar to bacterial two-component regulators. Science. 1993 Oct 22;262(5133):566–569. doi: 10.1126/science.8211183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan G., Newton A. FlbD of Caulobacter crescentus is a homologue of the NtrC (NRI) protein and activates sigma 54-dependent flagellar gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2369–2373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury S., Zielinski N. A., Ninfa A. J., Allen N. E., Jungheim L. N., Nicas T. I., Chakrabarty A. M. Inhibitors of two-component signal transduction systems: inhibition of alginate gene activation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):965–969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Stock A. M., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of the site of phosphorylation of the chemotaxis response regulator protein, CheY. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21770–21778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer H. D. Small broad-host-range gentamycin resistance gene cassettes for site-specific insertion and deletion mutagenesis. Biotechniques. 1993 Nov;15(5):831–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Newton A. Regulation of periodic protein synthesis in the cell cycle: control of initiation and termination of flagellar gene expression. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J. M., Newton A. Pseudoreversion analysis indicates a direct role of cell division genes in polar morphogenesis and differentiation in Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1991 Nov;129(3):623–630. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J. M., Newton A. Sequential regulation of developmental events during polar morphogenesis in Caulobacter crescentus: assembly of pili on swarmer cells requires cell separation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):409–415. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.409-415.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J. M., Newton A. Turning off flagellum rotation requires the pleiotropic gene pleD: pleA, pleC, and pleD define two morphogenic pathways in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):392–401. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.392-401.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens C. M., Shapiro L. An unusual promoter controls cell-cycle regulation and dependence on DNA replication of the Caulobacter fliLM early flagellar operon. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(6):1169–1179. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V. Nitrate regulation of anaerobic respiratory gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):425–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A., Koshland D. E., Jr, Stock J. Homologies between the Salmonella typhimurium CheY protein and proteins involved in the regulation of chemotaxis, membrane protein synthesis, and sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7989–7993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trach K., Chapman J. W., Piggot P., LeCoq D., Hoch J. A. Complete sequence and transcriptional analysis of the spo0F region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4194–4208. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4194-4208.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volz K. Structural conservation in the CheY superfamily. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 9;32(44):11741–11753. doi: 10.1021/bi00095a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Sharma P. L., Schoenlein P. V., Ely B. A histidine protein kinase is involved in polar organelle development in Caulobacter crescentus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):630–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Kiser G. L., Hartwell L. H. Mitotic checkpoint genes in budding yeast and the dependence of mitosis on DNA replication and repair. Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 15;8(6):652–665. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.6.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingrove J. A., Mangan E. K., Gober J. W. Spatial and temporal phosphorylation of a transcriptional activator regulates pole-specific gene expression in Caulobacter. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1979–1992. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]