FIGURE 3.
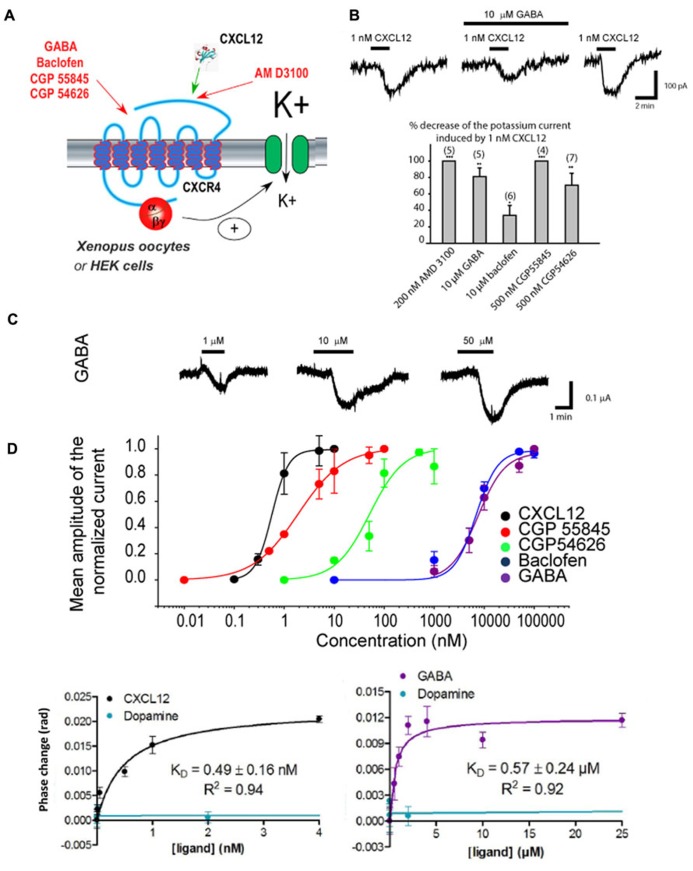
GABA and agonists/antagonists of the GABAB receptor are allosteric modulators of CXCR4. (A) Scheme showing the diverse agents acting on the CXCR4 receptor that have been tested. CXCR4 has been co-expressed together with GIRK channels in Xenopus oocytes and human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells. The activation of CXCR4 by the diverse agent tested was evaluated by measuring the amplitude of the GIRK current activated. (B) Results obtained in HEK293 cells expressing CXCR4 and reporting GIRK channel. Top: Traces recorded in response to the application of 1 nM CXCL12 with or without GABA. GABA inhibits partially the CXCL12 effect and this effect is reversible upon washout of GABA. Bottom: Histogram showing the allosteric actions of the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 compared to GABA and other agonists/antagonists of GABA B receptors. (C) Results obtained in Xenopus oocytes expressing CXCR4 and reporting GIRK channel. Top: Traces recorded in response to the application of three increasing GABA concentrations. Bottom: We took advantage of the agonist effect of GABA and of the GABA B agonists/antagonists in this expression system to build their concentration–response curve on CXCR4. (D) Back-scattering interferometry (BSI) results obtained on lipoparticles containing only CXCR4. Left: BSI reveals a K D of CXCL12 on its receptor of 0.49 ± 0.16 nM, which is coherent with the EC50 measured by our electrophysiological experiments. Dopamine, used as a negative control, does not bind to CXCR4. Right: BSI reveals that GABA can also directly bind to CXCR4 with a K D of 0.57 ± 0.24 μM, coherent with the EC50 measured in electrophysiology. Therefore, GABA can directly bind to CXCR4. Adapted from Guyon et al. (2013).