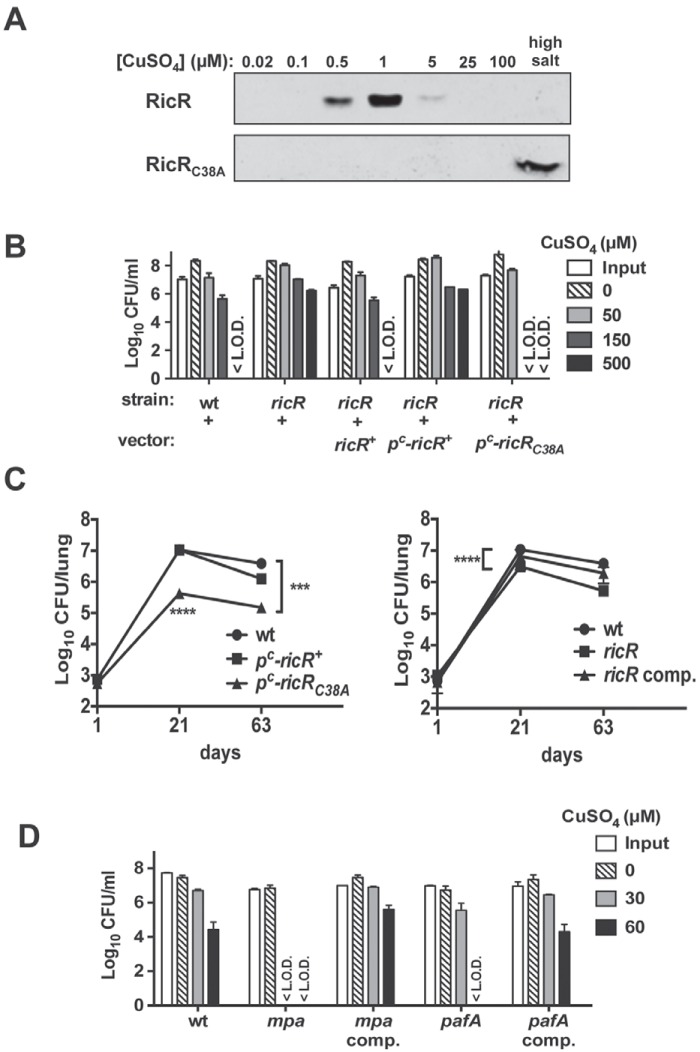
FIG 7 .
Repression of the entire RicR regulon sensitized M. tuberculosis to Cu and attenuated M. tuberculosis in mice. (A) DNA affinity chromatography shows that RicR dissociates from the lpqS promoter in the presence of Cu as previously described (top) while RicRC38A constitutively bound to DNA regardless of the presence of Cu (bottom). Protein was eluted from the DNA with sequential increasing amounts of CuSO4 or a high salt concentration (last). (B) A Cu sensitivity assay revealed that the pc-ricRC38A strain was hypersensitive to Cu. The WT CDC1551/pMV306 (empty vector), ricR/pMV306, ricR/pMV-ricR+, ricR/pMV-pc-ricR+, and ricR/pMV-pc-ricRC38A strains were tested for Cu sensitivity. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation of one experiment that was done three times. (C) Constitutive repression of the ricR regulon attenuated M. tuberculosis growth in mice. CFU counts in the lungs of C57BL/6 mice infected with the WT/pMV306, ricR/pMV-pc-ricR+, ricR/pMV-pc-ricRC38A, ricR/pMV306, or ricR/pMV-ricR+ (ricR comp.) strain are shown. The data were separated into two graphs for clarity but represent infections done within the same week. The WT infection in both panels represents the same experiment. The initial dose of infection was ~500 CFU/mouse. The data represent the means ± standard deviations at days 1 (n = 3), 21 (n = 4), and 63 (n = 4) postinfection. The WT and pc-ricRC38A data are representative of two independent infections. ****, P < 0.0001; ***, P < 0.001 (two-way analysis of variance with a Bonferroni posttest). (D) Proteasomal-degradation-defective strains were hypersensitive to Cu. The WT/pMV306 and mpa/pMV306, mpa/pMV-mpa+, pafA/pMV306, and pafA/pMV-pafA+ mutant H37Rv strains were exposed to Cu for 10 days. The data represent the means ± standard deviations of one typical experiment that was done three times. <L.O.D., below the limit of detection.