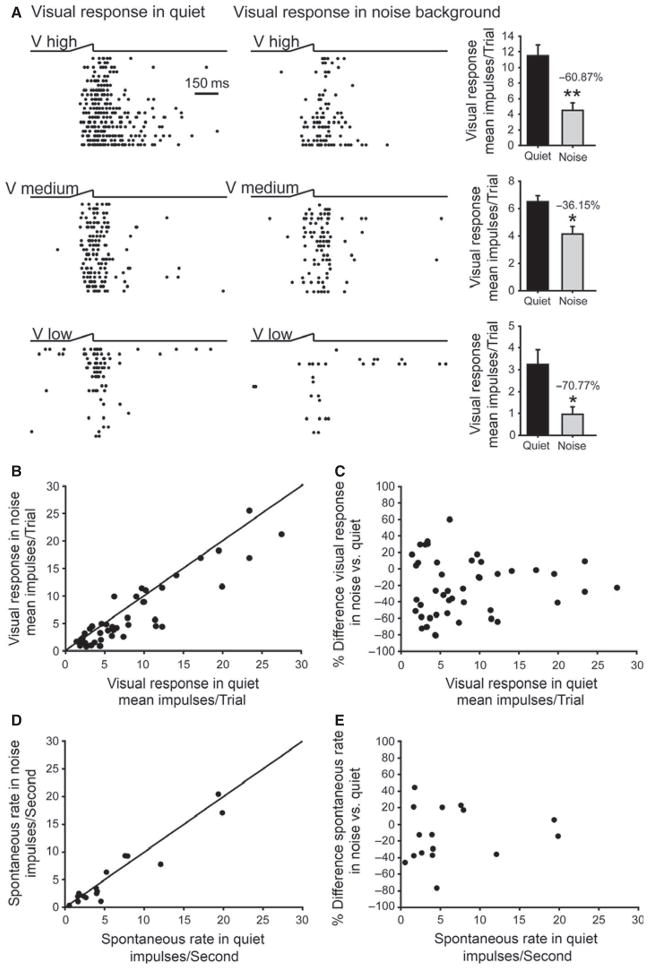
Fig. 2.
Visual responses in an omnidirectional noise-reared animal were depressed by background noise. (A) The visual responses of a visual–auditory neuron at three visual stimulus intensities (high, 3.47 cd/m2; medium, 1.44 cd/m2; low, 0.93 cd/m2) in the presence and absence of background noise equivalent to that in the rearing condition. Note the response depression at all three levels of stimulus effectiveness. (B) Comparison of the responses of a population of neurons to a visual stimulus in the noise background versus the same stimulus in quiet. Visual responses were significantly depressed by the background noise and most fell below the diagonal line of equality (Wilcoxon signed rank test, P ≤0.001, n = 48). (C) The percentage difference in each neuron between its visual response in noise and in quiet. (D) Comparison of the spontaneous activity recorded from each neuron in the presence of the background noise or in quiet. Spontaneous activity was slightly, albeit not significantly, depressed by the omnidirectional background noise stimulus (paired t-test, P = 0.194, n = 16). (E) The percentage difference between the spontaneous rates of each neuron in noise and in quiet.