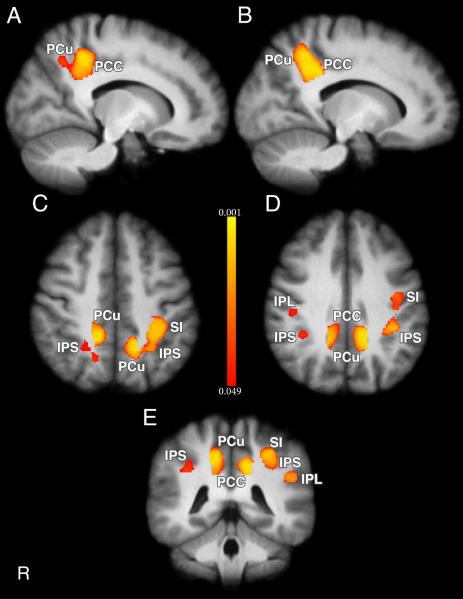
Figure 2.
Differences in regional grey matter density are inversely related to pain sensitivity in healthy subjects (n=116). VBM regression analysis revealed increased grey matter in subjects reporting low VAS pain ratings at 49°C. Subjects reporting high VAS pain ratings at 49°C exhibited less grey matter. A, B, Sagittal slices showing grey matter differences in right (Coordinates: 14, −44, 42) and left (Coordinates: −14, −48, 40) PCu (voxels (R) = 289, (L) = 335; p = 0.006) and right (Coordinates: 14, −42, 36) and left (Coordinates: −14, −44, 36) PCC (voxels (R) = 184, (L) = 199; p = 0.006). C, Horizontal slice showing grey matter differences in IPS (voxels (R) = 87, Coordinates: 24, −52, 46; voxels (L) = 408, Coordinates: −34, − 42, 46; p = 0.012), PCu, and SI (voxels = 417, Coordinates: −32, −36, 46; p = 0.012). D, Horizontal slice showing grey matter differences in right IPL (voxels = 51, Coordinates: 46, −24, 34, p < 0.05), IPS, PCC, PCu, and SI. E, Coronal slice showing grey matter differences in left IPL (voxels = 100, Coordinates: −50, −42, 28, p = 0.021), IPS, PCu, PCC, and SI. Color bar values correspond to p values. IPL = inferior parietal lobule, IPS = intraparietal sulcus, PCC = posterior cingulate cortex, PCu = precuneus, SI = primary somatosensory cortex.