Table 2.
Inhibition of BTK-94C binding to brominated albumin by modified tyrosine analogs.
| Chemical1 | Structure | Inhibition (IC50, µM) of BTK- 94C binding to brominated BSA2 |
|---|---|---|
| Tyr | 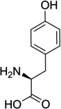 |
N.D.3 |
| 3-NO2-Tyr | 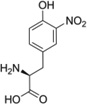 |
N.D. |
| 3-OH-HBA | 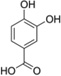 |
N.D. |
| 3-Br-HBA | 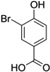 |
2 (0.3–6.3) |
| 3,5-Di-Br-HBA | 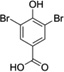 |
0.7 (0.2–1.5) |
| 3-Cl-Tyr | 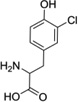 |
107.8 (70.6–145.3) |
| 3,5-Di-Cl-HBA | 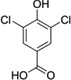 |
113.6 (53.4–550.8) |
Abbreviations: Tyr: L-Tyrosine; 3-NO2-Tyr, 3-nitrotyrosine; 3-OH-HBA, 3,4-dihydroxybenic acid; 3-Br-HBA, 3-bromo-4-hydroxybenzoic acid; 3,5-DiBr-HBA, 3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenzalehyde; 3-Cl-Tyr, 3-chlorotyrosine; and DiCl-HBA, 3,5-dichloro-4-hydroxybenoic acid.
The IC50 value is the median of triplicate analyses, each of which was fit to 3-parameter logistic binding curves. The 90% confidential intervals are shown are shown in parentheses.
N.D., inhibition was not detectable at any concentration examined (maximal concentration 1 mM).
