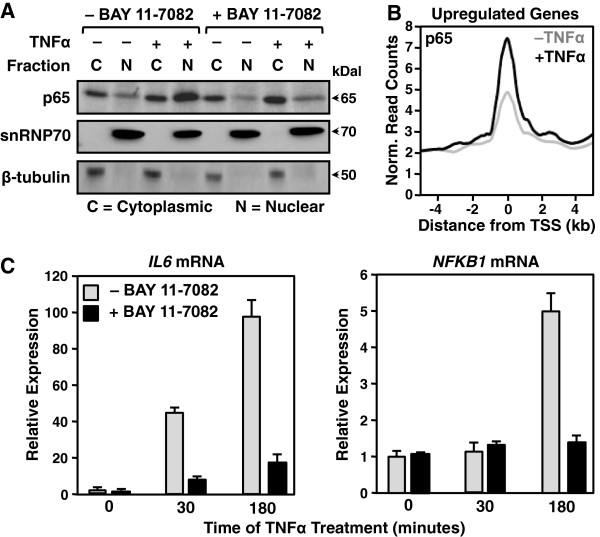
Figure 1.
TNFα stimulation of AC16 cells activates the NF-κB signaling pathway. A) Western blot of the NF-κB p65 subunit, snRNP70 (a nuclear marker), and β-tubulin (a cytoplasmic marker) using cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions from control and TNFα-treated AC16 cells (25 ng/ml for 30 min.) with and without the IKKα/β inhibitor BAY11-7082 (5 μM pretreatment for 1 hour). B) Metagene representation showing the average ChIP-seq read density of the NF-κB p65 subunit as a function of distance from the TSSs (± 4 kb) of upregulated protein-coding genes (defined by GRO-seq). The line shading indicates the control (grey) and TNFα-treated (black) conditions. C) RT-qPCR analysis of IL6 (left) and NFKB1 (right) mRNA expression in control and TNFα-treated AC16 cells (25 ng/ml TNFα for 30 or 180 minutes). The bar colors indicate the control (grey) and BAY11-7082-treated (black) samples. Each data point represents the mean + SEM for three independent biological replicates.