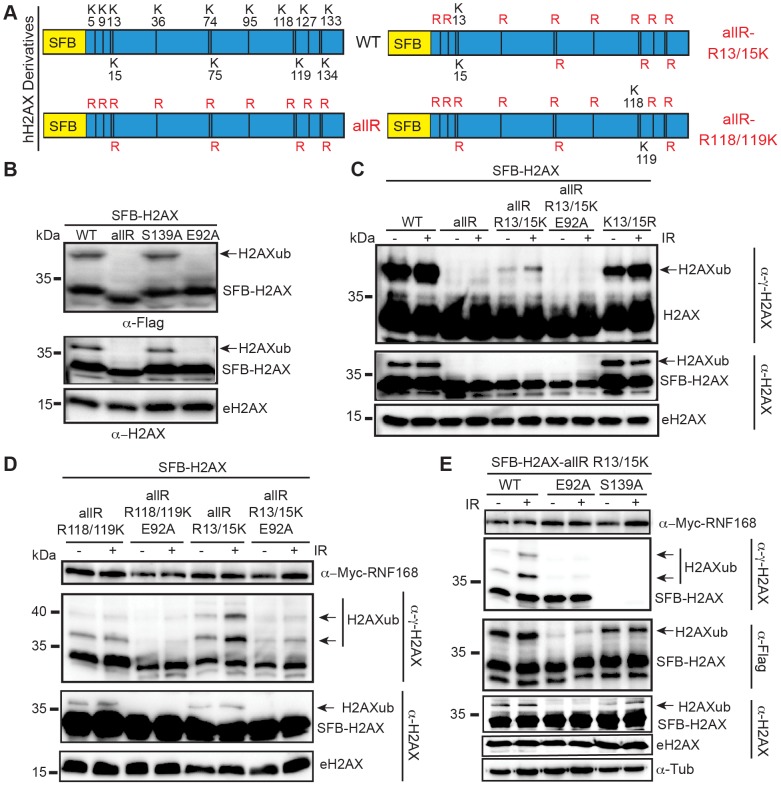
Figure 1. Mutation of the acidic patch impairs human H2AX and H2A ubiquitination.
(A) Schematic of all H2AX lysines (K) and mutant derivatives. allR represents an all lysine (K) to arginine (R) version of H2AX. Additional site-specific reversions from arginine to lysine within the allR H2AX derivate are indicated. (B) H2AX-allR and acidic patch mutation E92A reduces H2AXub. WT or E92A H2AX/H2A constructs were transfected into HEK293T cells and analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Arrows indicate ub forms. (SFB = S-tag, Flag epitope tag, and streptavidin-binding peptide tag; e = endogenous). Molecular weights (kDa) are indicated on the left of each panel. HEK293T cells were used for all cellular assays. (C) H2AX-K13/15 dependent ubiquitination requires the acidic patch. H2AX and derivatives were expressed in HEK293T cells (−) or (+) ionizing radiation (IR, 20 Gy). Samples were analyzed as in A 6 h post-IR treatment. (D) H2AX-K13/15 and K118/119-dependent ubiquitination requires the acidic patch. Cells were co-transfected with H2AX and derivatives along with Myc-RNF168 and analyzed as in C. (E) Phospho-competent H2AX S139 is not required in cis for H2AX K13/15ub. Cells were analyzed as in C. tub = tubulin loading control.