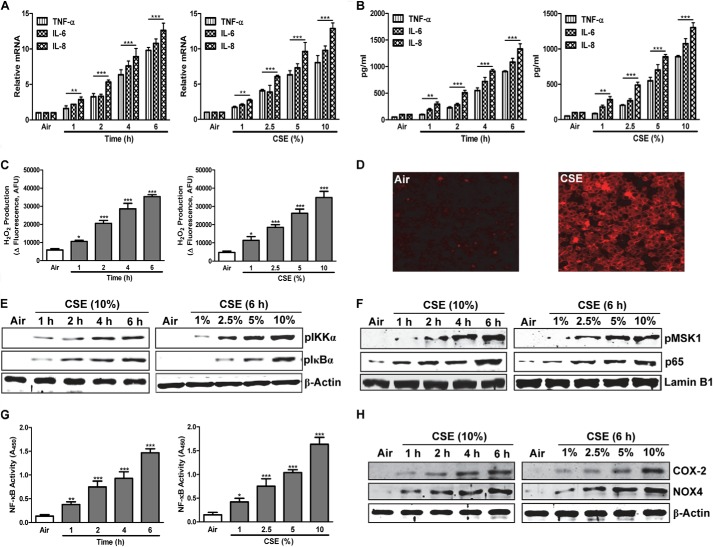
FIGURE 2.
CSE induces inflammatory responses and oxidative stress via up-regulation of NF-κB. A and B, shown are time courses and concentration-response relationships for CSE-induced cytokine/chemokine gene expression (A) and release (B). C, H2O2 production. G, DNA binding activity of NF-κB p65, measured by ELISA-based assay. E, F, and H, p-IKKα and p-IκBα (E), p-MSK1 and NF-κB p65 (F), and COX-2 and NOX4 protein levels (H), by Western blots. D shows ROS immunofluorescence in H292 cells exposed for 6 h to 10% CSE or air control. H292 cells were treated with various concentrations (1–10%) of CSE for 6 h or for 1–6 h with 10% CSE, as indicated. In A, RNA was isolated, and gene expression levels were analyzed by real-time PCR. B and C show levels measured in culture medium. E and H, in whole-cell extracts; F and G, in nuclear extracts. Data are representative of three independent experiments, with n = 3. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001.