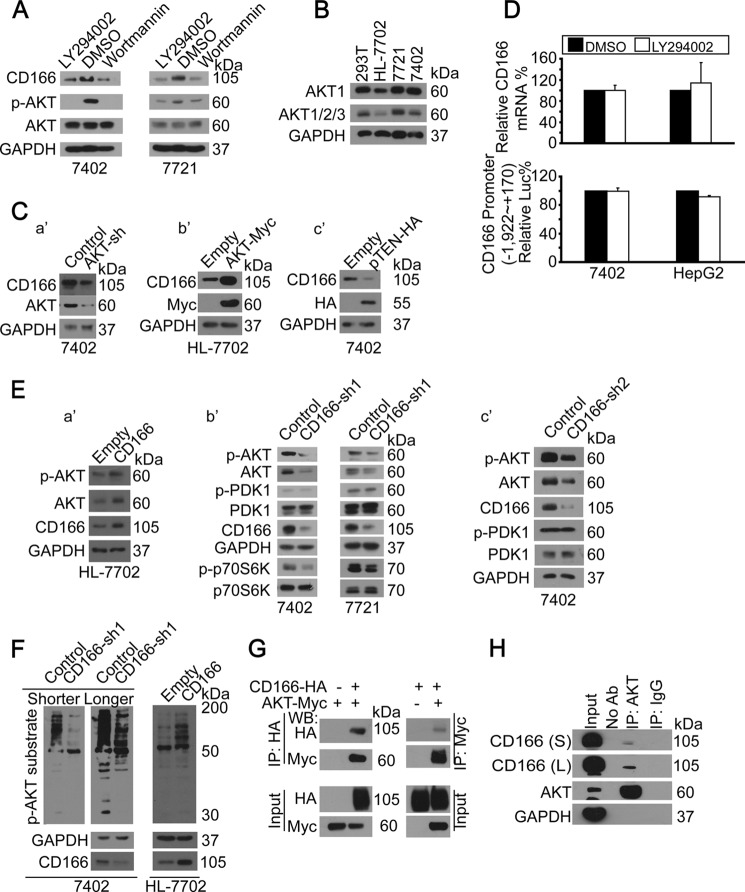
FIGURE 2.
Regulatory feedback between PI3K/AKT and CD166. A, inhibition of PI3K/AKT reduced CD166. Shown are Western blots of proteins as indicated in cells treated with DMSO, LY294002 (20 μm), or wortmannin (50 μm) for 24 h. B, AKT expression patterns in different cell lines. Shown are Western blots of AKT1 as well as AKT1/2/3 (pan-AKT) in different cell lines as indicated. C (a′–c′), AKT-regulated CD166. Western blots of CD166 in control and cells with either AKT knockdown (a′), AKT overexpressed (b′), or pTEN-HA overexpressed (c′). D, PI3K/AKT did not affect YAP gene transcription. YAP mRNA was detected by qPCR in Bel-7402 and HepG2 cells treated with either DMSO or LY294002 (20 μm) for 24 h (top). PI3K/AKT did not affect CD166 promoter activity. Luciferase activities from −1,992 to +170 relative to the transcription start site of the CD166 gene were measured in Bel-7402 and HepG2 cells treated with either DMSO or LY294002 (20 μm) for 24 h. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to that of Reniila (bottom). E (a′–c′), CD166-induced AKT expression. Western blots of p-AKT/AKT in control (transfected with empty vector) and HL-7702 cells with CD166 overexpressed (a′). Shown are Western blots of proteins as indicated in control cells (infected with GFP shRNA) and cells with CD166 knocked down (infected with CD166-sh1 (b′) and CD166-sh2 (c′), respectively). F, CD166-induced AKT phosphorylation activity. Shown are Western blots of p-AKT substrate using an antibody specific for p-AKT substrate in control (infected with GFP shRNA) and Bel-7402 cells with CD166 knocked down (infected with CD166-sh1; left). S, shorter exposure; L, longer exposure. Western blots of p-AKT substrate in control (transfected with empty vector) and HL-7702 cells with CD166 overexpressed (right). G, AKT bound to CD166. CD166-HA was co-transfected with AKT-Myc into Bel-7402 cells, as indicated. CD166 and AKT associations were examined by reciprocal co-IP, as indicated. H, endogenous CD166 was immunoprecipitated with anti-AKT antibodies (ab), and co-immunoprecipitation of CD166 was shown by anti-CD166 Western blot. A control IgG was used as the negative control for immunoprecipitation. S, shorter exposure; L, longer exposure.