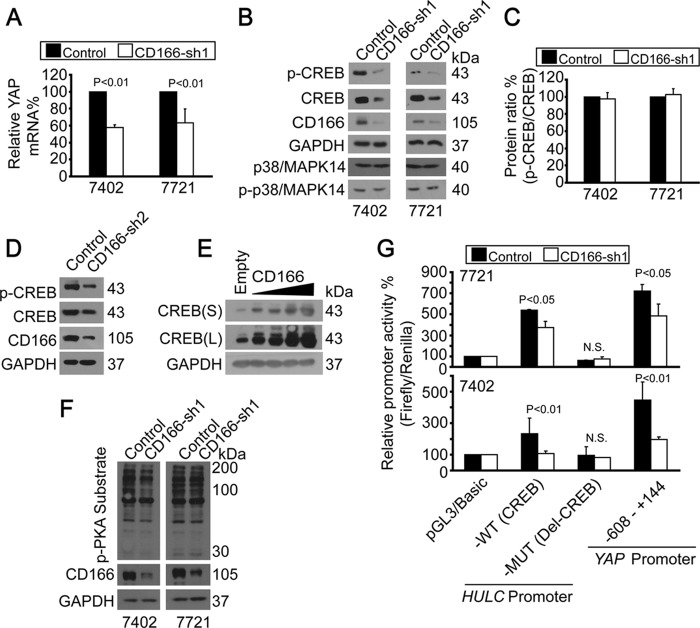
FIGURE 5.
CD166 regulated YAP gene transcription via CREB. A, YAP mRNA levels were detected by qPCR without (control; infected with GFP shRNA) or with CD166 knocked down (infected with CD166-sh1) in Bel-7402 or SMMC-7721 cells. B, CD166 regulated CREB. Shown are Western blots of proteins as indicated in control cells (infected with GFP shRNA) and Bel-7402 or SMMC-7721 cells with CD166 knockdown (infected with CD166-sh1). C, quantification of p-CREB/total CREB ratio from B. D, knockdown of CD166 by sh2 reduced both p-CREB and total CREB in Bel-7402 cells. E, CD166 dose-dependently increased CREB expression in HL-7702 cells. S, shorter exposure; L, longer exposure. F, CD166 did not affect PKA activity. Phospho-PKA substrates were tested in control (infected with GFP shRNA) and Bel-7402 or SMMC-7721 cells with CD166 knocked down (infected with CD166-sh1). G, CD166 regulated HULC and YAP promoter activities. Promoter activities were tested from luciferase constructs as indicated in control (infected with GFP shRNA) and SMMC-7721 (top) or Bel-7402 (bottom) cells with CD166 knocked down (infected with CD166-sh1). Error bars, S.D.