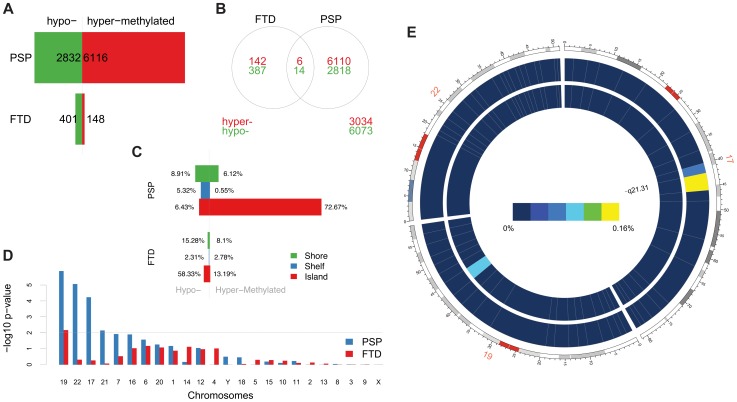
Figure 1. Differentially methylated probes (DMPs) identified in disease vs. control comparisons.
(a) Barplots representing the numbers of differentially methylated probes (DMPs) identified in each disease group vs. controls (Benjamini-Hochberg-adjusted p-value ≤0.05). The number of DMPs indicated in PSP vs. Control comparison is the union set of DMPs identified in dataset #1 and dataset #2. Red bars: hypermethylated DMPs, green bars: hypomethylated DMPs. (b) Venn diagram representing the overlap between DMPs in FTD vs. controls and PSP vs. controls. Red numbers: hypermethylated DMPs; green: hypomethylated DMPs. (c) Barplots representing DMPs classified by probe type. CpG island probes are overrepresented in both FTD vs. controls and PSP vs. controls. (d) Chromosome enrichment analysis: DMPs are significantly enriched in chromosomes 19, 22, and 17, only in PSP vs. controls (y axis: −log10 (p-value), hypergeometric test). (e) Circos plot [65] of chromosomes 19, 22, and 17 showing regional enrichment of DMPs (PSP vs. Control comparison, BH adjusted p-value ≤0.05, absolute average beta difference (aβD)>0.1) in one region on chromosome 17. Each chromosome was divided into 20 regions, which contain the equal number of CpG probes. Regions were colored according to the DMP density. Blue: low DMP density, yellow: high density. Circles from inner to outer represent FTD, PSP vs. controls, respectively.