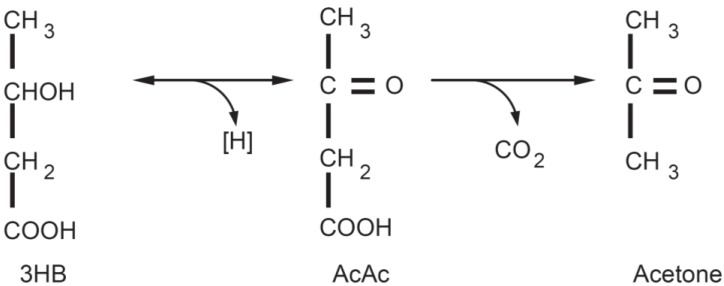
Figure 1.
Ketone bodies: acetoacetate (AcAc) is the principle ketone body. It is produced and utilized during intermediary metabolism and other ketone bodies are derived from it. Acetone is produced by the spontaneous decarboxylation of acetoacetate and is important from the clinical point of view because it is responsible for the fruity sweet odour of infant ketoacidosis. β-Hydroxybutyric acid is produced via the reduction of AcAc. From a strictly biochemical point of view it is not actually a ketone body since the ketonic moiety is reduced to a hydroxyl group; it is though grouped among the ketone bodies. 3HB is relatively stable biochemically and is transported to the tissues where it is reconverted to AcAc.