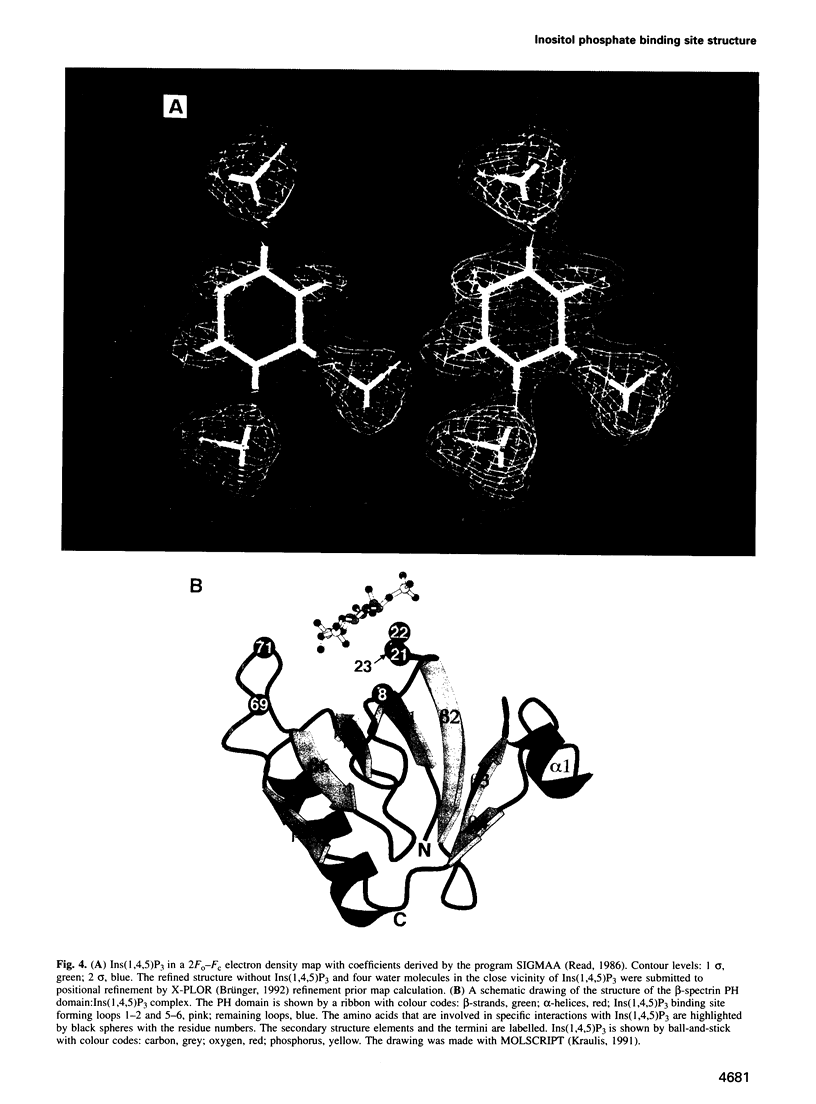
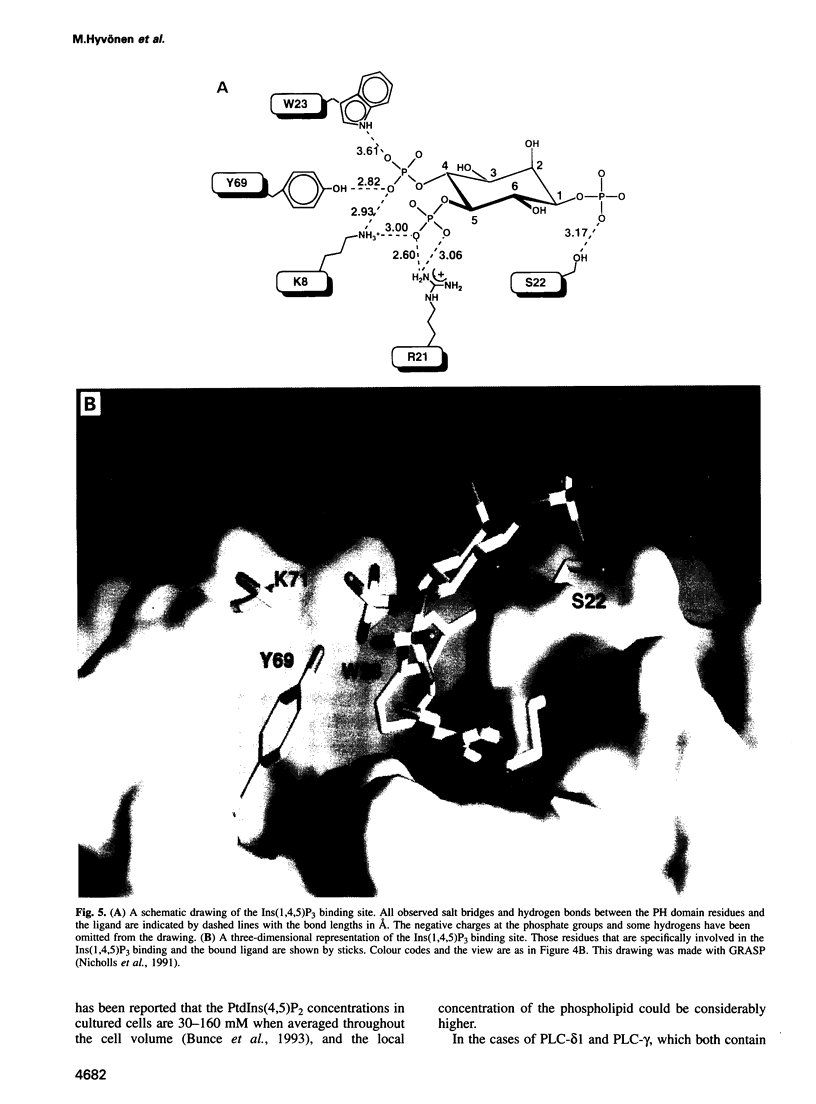
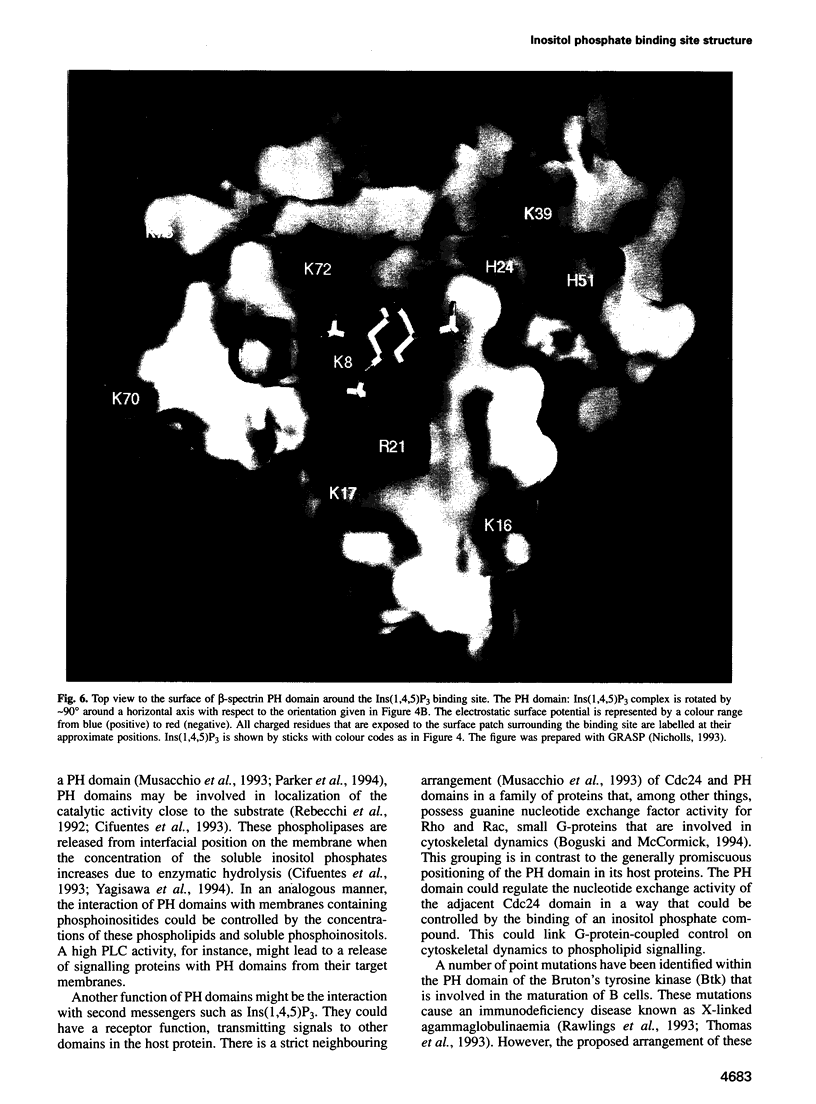
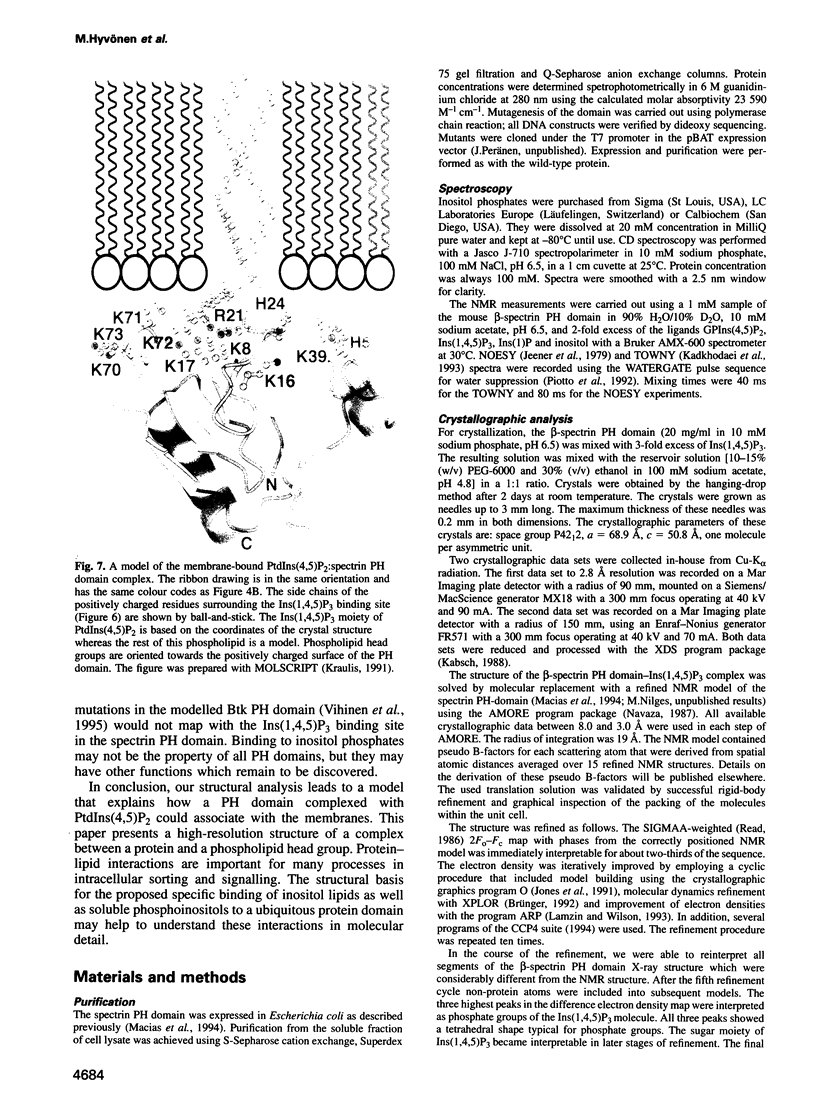
Abstract
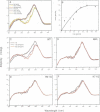
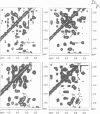
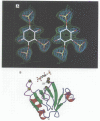
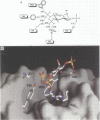
Phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate has been found to bind specifically to pleckstrin homology (PH) domains that are commonly present in signalling proteins but also found in cytoskeleton. We have studied the complexes of the beta-spectrin PH domain and soluble inositol phosphates using both circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and X-ray crystallography. The specific binding site is located in the centre of a positively charged surface patch of the domain. The presence of 4,5-bisphosphate group on the inositol ring is critical for binding. In the crystal structure that has been determined at 2.0 A resolution, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate is bound with salt bridges and hydrogen bonds through these phosphate groups whereas the 1-phosphate group is mostly solvent-exposed and the inositol ring has virtually no interactions with the protein. We propose a model in which PH domains are involved in reversible anchoring of proteins to membranes via their specific binding to phosphoinositides. They could also participate in a response to a second messenger such as inositol trisphosphate, organizing cross-roads in cellular signalling.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunce C. M., French P. J., Allen P., Mountford J. C., Moor B., Greaves M. F., Michell R. H., Brown G. Comparison of the levels of inositol metabolites in transformed haemopoietic cells and their normal counterparts. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 1;289(Pt 3):667–673. doi: 10.1042/bj2890667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes M. E., Delaney T., Rebecchi M. J. D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate inhibits binding of phospholipase C-delta 1 to bilayer membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1945–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes M. E., Honkanen L., Rebecchi M. J. Proteolytic fragments of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-delta 1. Catalytic and membrane binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11586–11593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. B., Ren R., Baltimore D. Modular binding domains in signal transduction proteins. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. H., Bennett V. Identification of two regions of beta G spectrin that bind to distinct sites in brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 11;269(6):4409–4416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divecha N., Irvine R. F. Phospholipid signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing A. K., Driscoll P. C., Gout I., Salim K., Zvelebil M. J., Waterfield M. D. Three-dimensional solution structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from dynamin. Curr Biol. 1994 Oct 1;4(10):884–891. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson K. M., Lemmon M. A., Schlessinger J., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure at 2.2 A resolution of the pleckstrin homology domain from human dynamin. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushman D., Cahill S., Lemmon M. A., Schlessinger J., Cowburn D. Solution structure of pleckstrin homology domain of dynamin by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):816–820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Hyvönen M., Musacchio A., Saraste M., Birney E. PH domain: the first anniversary. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Sep;19(9):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. E., Hajduk P. J., Yoon H. S., Fesik S. W. Pleckstrin homology domains bind to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1994 Sep 8;371(6493):168–170. doi: 10.1038/371168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz D. W., Ryan M., Bullock T. L., Griffith O. H. Crystal structure of the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus in complex with myo-inositol. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 15;14(16):3855–3863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingley E., Hemmings B. A. Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains in signal transduction. J Cell Biochem. 1994 Dec;56(4):436–443. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240560403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Inglese J., Stone W. C., Lefkowitz R. J. The binding site for the beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins on the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8256–8260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamzin V. S., Wilson K. S. Automated refinement of protein models. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1993 Jan 1;49(Pt 1):129–147. doi: 10.1107/S0907444992008886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macias M. J., Musacchio A., Ponstingl H., Nilges M., Saraste M., Oschkinat H. Structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from beta-spectrin. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):675–677. doi: 10.1038/369675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Rice P., Thompson J., Saraste M. The PH domain: a common piece in the structural patchwork of signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90071-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Hemmings B. A., Gierschik P. PH domains and phospholipases--a meaningful relationship? Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):54–55. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotto M., Saudek V., Sklenár V. Gradient-tailored excitation for single-quantum NMR spectroscopy of aqueous solutions. J Biomol NMR. 1992 Nov;2(6):661–665. doi: 10.1007/BF02192855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings D. J., Saffran D. C., Tsukada S., Largaespada D. A., Grimaldi J. C., Cohen L., Mohr R. N., Bazan J. F., Howard M., Copeland N. G. Mutation of unique region of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in immunodeficient XID mice. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):358–361. doi: 10.1126/science.8332901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M., Peterson A., McLaughlin S. Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-delta 1 binds with high affinity to phospholipid vesicles containing phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 29;31(51):12742–12747. doi: 10.1021/bi00166a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Hyvönen M. Pleckstrin homology domains: a fact file. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1995 Jun;5(3):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(95)80104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Sideras P., Smith C. I., Vorechovský I., Chapman V., Paul W. E. Colocalization of X-linked agammaglobulinemia and X-linked immunodeficiency genes. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):355–358. doi: 10.1126/science.8332900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timm D., Salim K., Gout I., Guruprasad L., Waterfield M., Blundell T. Crystal structure of the pleckstrin homology domain from dynamin. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Nov;1(11):782–788. doi: 10.1038/nsb1194-782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touhara K., Inglese J., Pitcher J. A., Shaw G., Lefkowitz R. J. Binding of G protein beta gamma-subunits to pleckstrin homology domains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10217–10220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihinen M., Zvelebil M. J., Zhu Q., Brooimans R. A., Ochs H. D., Zegers B. J., Nilsson L., Waterfield M. D., Smith C. I. Structural basis for pleckstrin homology domain mutations in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 7;34(5):1475–1481. doi: 10.1021/bi00005a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. S., Shaw R., Winkelmann J. C., Shaw G. Binding of PH domains of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase and beta-spectrin to WD40/beta-transducin repeat containing regions of the beta-subunit of trimeric G-proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Aug 30;203(1):29–35. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagisawa H., Hirata M., Kanematsu T., Watanabe Y., Ozaki S., Sakuma K., Tanaka H., Yabuta N., Kamata H., Hirata H. Expression and characterization of an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate binding domain of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C-delta 1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):20179–20188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon H. S., Hajduk P. J., Petros A. M., Olejniczak E. T., Meadows R. P., Fesik S. W. Solution structure of a pleckstrin-homology domain. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):672–675. doi: 10.1038/369672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]